views
Caring for Indoor Potted Plants

Choose potting soil that is formulated for indoors. It can be tempting to use dirt from your yard or the same potting soil that you use outside; however, indoor plants have different needs than outdoor plants. Make sure that your soil is made for indoor plants because it will be lightly packed enough for the plants to grow while still tight enough to hold in the water. Change your soil every year or two. You should also check to make sure that your plant does not require special soil, such as clay, loam, sand, or peat. These soils hold different amounts of water to meet the needs of plants that may struggle in traditional soil. Additionally, you can find soil with added nutrients for your indoor plant.
Make sure the plant gets the right amount of light. Some indoor plants require a lot of light and need to be placed in a window that gets full sun, while others would wilt under all those rays. Check your plant's needs to ensure that they are being met. Don’t assume that a plant needs to be in a window. Some plants thrive in low light. Check to make sure that the window you choose for your full sun plant gets several hours of sunlight. Sometimes windows are sunny for part of the day but in shade for the majority of the day. Choose a day when you’re home all day to check back at regular times to see how the light levels are. If your home doesn’t get adequate light, you can try a UV lamp.

Water your plants according to their needs. Some plants need daily watering, while others need weekly, biweekly, or monthly watering. Check the care information for your plant to find out how much water it needs. Many people think that they can’t go wrong by watering frequently, but you can overwater a plant just as easily as not water it enough. Overwatering drowns the plant.
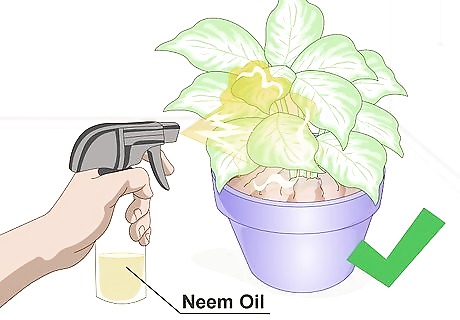
Prevent pests. You may think that your plants are safe from pests because they’re inside, but that is untrue. Think about all of the times that bugs have found their way into your house. Pests that can harm your plants can easily come in as well. To prevent pests, spray your plants once or twice a week with neem oil to keep them safe from mites and mealybugs. You can also purchase a commercial pesticide formulated for indoor plants.
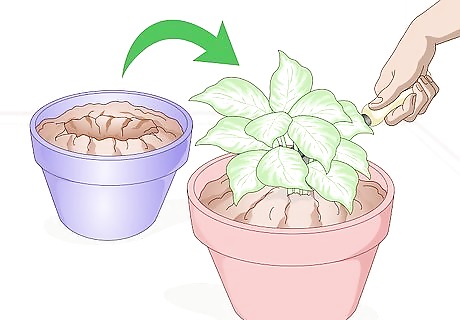
Choose the right pot. As your plant grows, you should transplant it into larger pots that better suit the size of the plant so that the roots don’t twist in on themselves, suffocating the plant. Additionally, the pot that you use should be the right material and the right size for your plant because the pot size can determine the amount of moisture that the plant receives. When transplanting your plants, always shake the old dirt loose from the roots. If the inner roots are twisted, gently loosen them so that they are able to grow in the new pot. For example, plastic pots hold onto water, while clay pots don’t. It’s best to use a plastic pot only if you have a plant that needs a lot of water, because one that doesn’t will drown. Choose a pot that is 2-4 inches (5-10 centimeters) larger in diameter than your plant because extra soil will mean extra moisture, which could overwater your plant.
Fertilize your plants monthly. Plants’ soil becomes less nutritious over time, and indoor plants often struggle to replenish those nutrients. Fertilize your indoor plants while they’re growing and/or flowering once a month to keep them as healthy as possible.
Prune your plants to maintain a desired shape and size. Plants have different growing tendencies and requirements for thriving. Regardless of the type of plant, it’s best to use the plant’s natural lifecycle as a guide for pruning. If you notice, for example, that your indoor plants are growing quickly during a certain time period, it may be a good idea to trim any shoots as soon as you notice them.
Caring for Outdoor Potted Plants

Place them in the sun. Plants need sun in order to convert carbon dioxide and water into their food and energy. While potted plants are often easy to arrange on porches and balconies, they still need access to proper sunlight. Check your plant’s insert or information to see if it needs full sun or can thrive in the shade. Remember that shade-friendly plants still need indirect sunlight to stay alive.

Choose a good potting soil. Your plant will need soil that is formulated for potted plants because they are growing in a different situation than plants that are in the ground. One of the ingredients that your soil will need is decaying organic matter, which is in most good potting soils. Organic matter will break down into the nutrients that your plant needs to absorb to be healthy.

Add fertilizer. Potted plants require more added nutrients than plants that are in the ground, so regularly add fertilizer to your soil. Supplement your soil by adding organic matter either through a commercial fertilizer or your own composting. Some fertilizers are liquid and can be added directly to the watering can you use to water your plants, making it an easy part of your plant care routine.

Prune the dead parts off of your plants. If your plant has wilted leaves or buds, remove them from the rest of the plant. This will encourage new growth instead of allowing your plant to shrivel up.

Avoid sudden transitions from indoors. If you start a plant indoors or have moved it inside over the winter, don’t move it permanently outdoors without a transition period. A plant that is accustomed to living indoors is not equipped to survive outside. The environment is different and can cause the plant to wither; additionally, the rain levels can cause overwatering.

Protect from pests. Choose a chemical-free pesticide treatment that’s formulated to protect your plants. Different plants attract different pests, so read the label to make sure that you pick the right product. Don’t try to kill all bugs, as some can be friendly to your garden.
Caring for a Garden
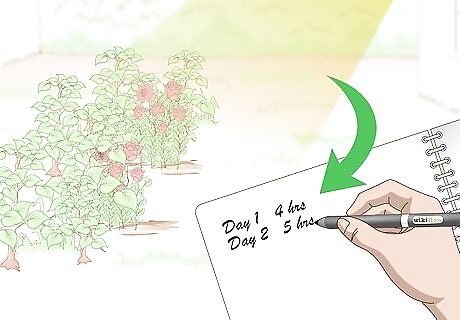
Chart how much sun that your garden will get. Spend a day tracking the sun as it travels over your garden or the spot you’d like to use. Many plants thrive with lots of sun, so look for shady trees or overhangs that may limit the sun. Additionally, notice if the shadow of your house or other large structures falls across your garden for part of the day, as this can limit the amount of sunlight that your plants receive. Once you know where the sunny spots are, you can ensure that your plants get enough sun. If the plants you choose require full sun, make sure that your garden will get at least five hours of direct sunlight each day. Consider choosing a new spot for your garden if it doesn’t get proper sun. Alternatively, you can try adding more plants that thrive in the shade or in part sun.

Add decaying organic matter. Your plants need dead plants and other rotting organic debris to break down in the soil so that the plants can absorb the nutrients. In addition to allowing dead leaves to stay in the garden, you can also buy fertilizer or compost material, or you can create your own compost pile with dead leaves and food scraps. If you clean up your garden, add the material to your compost pile. Avoid putting debris with weed seeds into your compost.
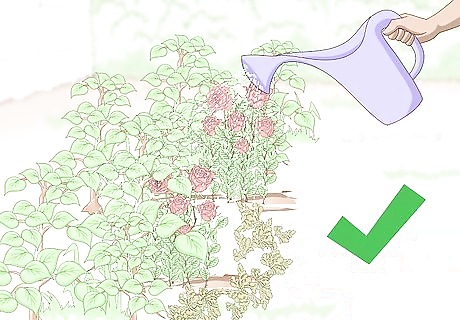
Water your garden. You need to give your plants enough water to meet their needs. Since the plants are outside, they may also be getting rain water. Adjust your watering schedule to account for the rain. Your soil should be moist but not soaked. With an outdoor garden, you can get a sprinkler system to ensure that they are regularly watered. Don’t water your garden if it rained that day. If a heavy storm comes through, allow the soil to dry some before you resume watering. If you live in a dry climate, give newly planted plants extra water for the first few weeks they’re in the ground.
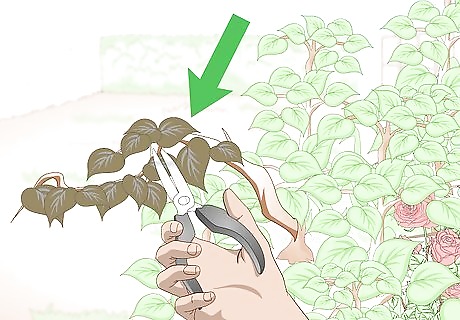
Prune your plants during winter or when they’re overgrown. Plants have different life cycles and growing speeds, so they require different pruning times. Prune your flowering plants after they have flowered to remove spent blooms and shape for next season. Prune any trees that you have during the winter, but remove dead limbs during the growing season when they are easier to identify.

Check the pH of your soil. Test your soil to see if it’s in a good range for plant growth. If not, you can amend the soil by adding compost, manure, or alfalfa meal to your soil, which all contain nitrogen. The nitrogen will lower the pH to 6.5 over time.



















Comments
0 comment