views
Sizing to the Original Chain
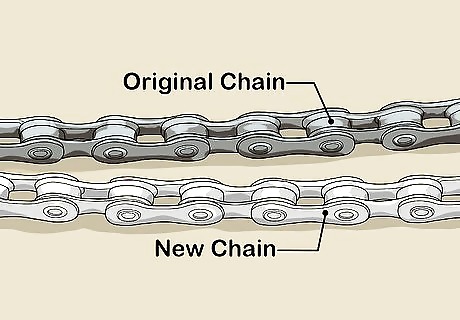
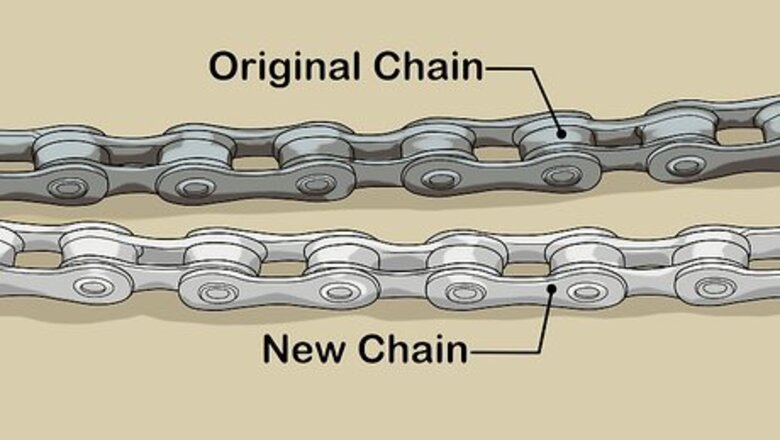
Lay the original chain side by side next to your new chain. If the original chain is the length you want the new chain to be, lay them next to each other so the plates are on their sides. Ensure that the plates on each chain line up. If you're using a master link chain, insert the master link so your measurement is accurate. For example, line up an outer plate with an outer plate or an inner plate with an inner plate.
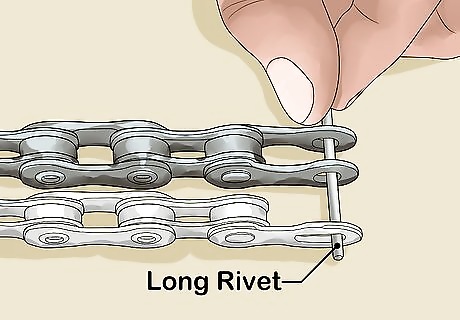
Line up both chains. Insert a metal skewer or long rivet through the end of your chains that you won't be cutting through. The skewer will hold the chains together and keep rivets lined up while you're preparing to measure and cut.
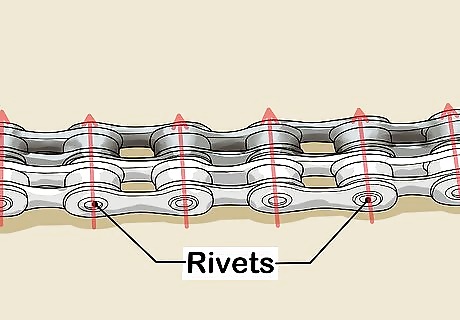
Match the rivets on the chains. Because the original chain may have gotten longer over time, slide the rivets on that chain so they're directly next to the rivets on the new chain.
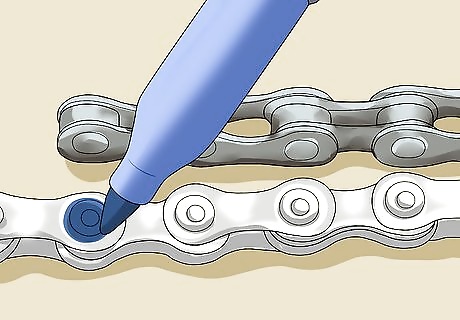
Locate and mark where to cut on the new chain. Once you've matched the rivets, you should clearly see where the original chain ends. Push the new chain down so the plates are facing you and use a marker to draw around the rivet that you'll cut. This rivet should match the rivet on the end of the original chain. Once you've cut or sized the new chain, it's ready to put on your bike.
Using the Largest Cog and Chainring
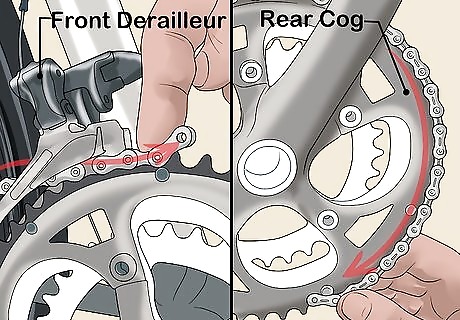
Move the derailleur gears and wrap the new chain around the rear cog. Move the front derailleur over the biggest front chainring and shift the rear derailleur to the smallest cog or sprocket. Drape the new chain around the biggest cog in the back. If you're using a connection rivet chain, move the end with the outer plate towards the front chainring. Keep threading the chain until the end is at the 5:00 position. If you're using a chain with a master link, put half of the master link in the plate.
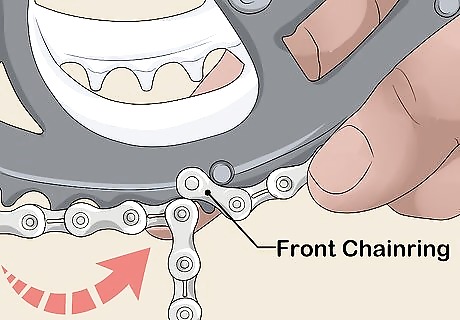
Pull the bottom of the chain to the front chainring. Gently tug on the lower portion of the chain and pull it onto the front chainring. Engage the chain on the front chainring so the rivet from the bottom of the chain meets the end of the top part of the chain. You won't need to pull the chain along the rear derailleur for this method.
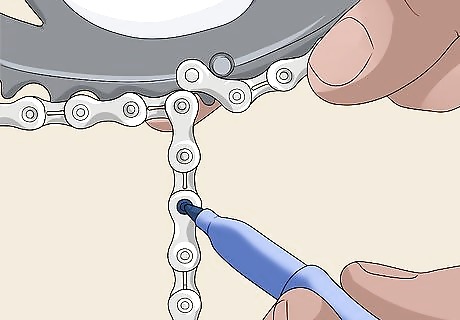
Find the cutting point for the chain. Locate the closest outer plate and inner plate where the chains meet. Use a marker to circle the rivet that can join the 2 chains. Then count 2 rivets down along the excess length of the chain. You'll cut the chain at this point, so consider drawing a line on it with a marker. Use your chain cutting tool to cut the chain to size. The 2 rivets will equal about 1 inch (2.5 cm), which should be enough of an adjustment for a rear derailleur.
Calculating the Chain Length
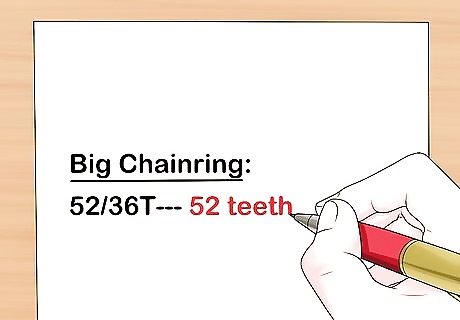
Write down how many teeth the big chainring has. Look on the big chainring to find its measurements. The number of teeth is designated by a number with a T following it. Use the first number on the big chainring at the front. For example, if your big chainring says 52/36T, it has 52 teeth. The full equation for calculating the chain length is as follows: (chainstayx2) + (chainring/4) + (rear sprocket/4) = correct chain length
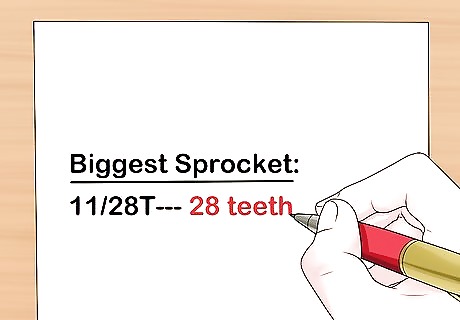
Write down how many teeth the biggest sprocket at the rear has. Check the second number on the sprocket to find how many teeth it has. For example, if you see 11/28T, it has 28 teeth.
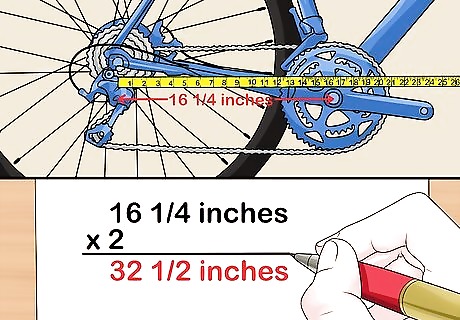
Measure the length of the chainstay and multiply it by 2. Pull a tape measure from the center of the rear axle to the center of the crank bolt. Write down the length to the closest 1/8th or 0.125 of an inch to give you the length of the chainstay. Multiply this number by 2 and write it down. For example, if your chainstay is 16 1/4 inches or 16.25 inches, multiply that by 2 to get 32 1/2 (32.5) inches. You'll need to write down the measurement in inches so you can use the equation. Once you've gotten the result, you can convert it to metric, if desired.
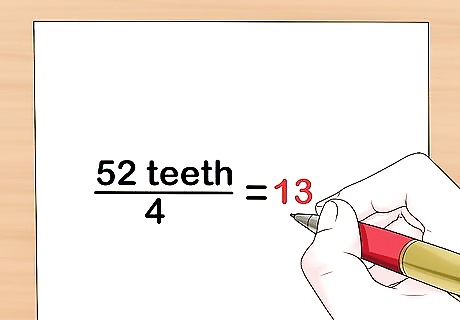
Divide the number of teeth on the biggest chainring by 4. Refer to the number of teeth that you wrote down. For example, if it has 52 teeth, divide it by 4 to get 13. Write this number down. Depending on the sprocket or chainring, you may have an odd number to divide by 4. The calculation will still work out if you have a decimal.
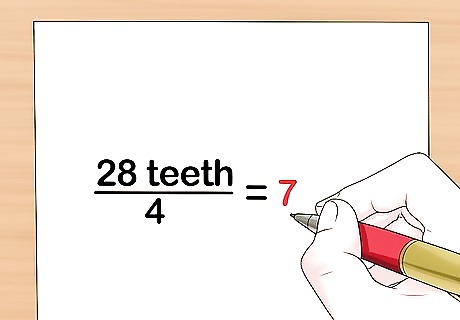
Divide the number of teeth on the biggest rear sprocket by 4. Look at the number you of teeth you wrote down for the rear sprocket. If your sprocket had 28 teeth divided by 4, you'd write down 7. You may not get a whole number if the sprocket has an odd number of teeth.
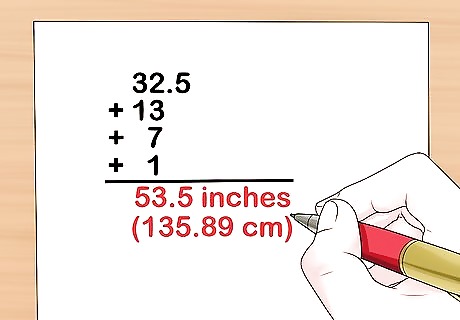
Add your modified numbers plus 1 inch (2.5 cm) to get the chain length. Add the multiplied chainstay length, the divided number of teeth for the chainring and rear sprocket, and add 1 (or 2.5 cm). The result is the ideal chain length for your bike. For example, you'd add 32.5, 13, 7 and 1 to get 53.5. The length of the chain should be 53.5 inches or 135.89 cm.




















Comments
0 comment