
views
Sizing and Cutting the Wood

Decide how large (or small) you want your planter box to be. Your decision should be based on how many plants you want to have in each planter, as well as the size of the area where you will be putting your planter. For this article, we will build a smaller box that is about 4 feet by 2 feet (121.9 by 60.9cm).

Purchase your wood. Untreated wood or cedar will work well for this project as they are both easy to work with and can hold up against the natural elements your planter will be exposed to. For a small 4x2 ft (121.9x60.9 cm) planter, you can buy a 12-foot (365.76-cm) board, which you will cut down to form the sides of the planter. The width should be at least 10 inches (24 cm).You will also need a piece that will act as the bottom or floor of the planter if your planter is going to be used on a deck or similar surface. If the box will be over soil, you can place a layer of flattened cardboard boxes on the bottom to act as a weed barrier. Pressure-treated lumber contains chemicals that will kill plants in the box and can things like arsenic to your food if you are growing vegetables. A safe alternative is using ACQ-treated wood, a process which does not use any toxic chemicals.

Cut the wood down to the right sizes. Use a measuring tape to measure out each side. Mark the places where you will make your cut with a pen or pencil. Use an electric saw or standard hand saw to cut the pieces to size (two 2 foot boards and two 4 foot boards), taking care to make the cuts as straight as possible. If you do not have a saw of any kind, or prefer to not make the cuts yourself, you can ask the workers where you purchased your wood to cut it down to the measurements you need. You may need to pay a small fee, but some lumber and hardware stores will cut your planks down to size for free.
Attaching the Boards
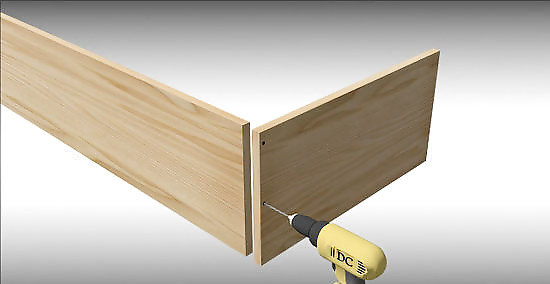
Create pilot holes in two of the boards. Pilot holes are holes drilled into the wood to ensure that the wood won’t splinter when you insert the screws into it. You only need to do this on the two end boards (the shorter boards). You should make three pilot holes, 3/4 inch (1.91 cm) from the end edge of the board. The middle hole should be centered in the middle of the width of the board.

Fasten the boards using galvanized screws. Galvanized screws are better for outdoor planters because the galvanized metal can stand up to the elements and will not rust. Line the boards up so that the boards with the pilot holes are positioned on the outside corners. Use a drill and drill bit to make sure that each screw goes through each hole and into the adjoining board. You can also use a screwdriver, rather than a drill and drill bit.

Measure the inside length and width to determine the size of the bottom of the box. With these measurements, cut your bottom board using a saw. Place the board inside the box. Use a drill and galvanized screws to attach the bottom board through the sides of the box. Remember, this is only necessary if you plan to put the planter on a deck or similar surface.

Drill drainage holes in the bottom of the box. Turn your now fully-formed box over and use your drill to create four or five drainage holes in the bottom of the box. These holes are very important, as most plants will develop diseases if they get ‘soggy feet’, meaning that their roots sit in very wet soil for too long. If you have constructed a much larger planter box, you should consider adding a few more drainage holes. Again, if your planter will be over soil, this is not necessary. Simply use flattened cardboard as the bottom of your box.
Adding the Finishing Touches

Place a layer of nylon or vinyl screen inside the planter. Doing this will protect the wood of your planter. Cut the screen so that it is the same size as the board you used for the bottom of the planter. Lay it in the bottom of the planter and fix in place with some small nails. Make sure that you remember to drill drainage holes in the screen that line up with the drainage holes in the bottom board if your box has a bottom.

Sand any rough edges. Doing this will give your box a nice finished look, but it is not absolutely necessary to do. Take a sander or a piece of sandpaper and run it along the edges and corners of the box. Run it along the sides of the boards to vanquish any potential splinters.

Paint, prime, or stain the outside of your planter. Pick out some paint that matches your backyard or home’s decor, or stain your planter to really bring out the wood’s colors. You can also choose to leave your wood alone, as cedar is a beautiful wood all by itself. Do not treat the inside of your planter, as this may contaminate the soil and your plants. Instead, use a plastic liner (with holes) to protect the wood.

Add a thin layer of gravel, then add the compost or potting soil. The gravel will help to drain the planter box. The type of soil or compost you use will depend on the types of plants or flowers you intend to add to your planter box.

Add your flowers, plants, or whatever seeds you plan to cultivate. Don't forget to water! For ideas on types of flowers and plants you can add to a planter box, click here.

Enjoy your new planter box!




















Comments
0 comment