views
Choosing the Best Location
Select a sunny area. If you have a lot of land options, you can select the vegetables you want to grow and find the perfect spot. If you are limited with land, then the spot will determine what will grow there. Ideally, you should opt for a location that is sunny for at least six hours a day. Evaluate your options and select your crops accordingly. Your location in the world also determines the type of plants and/or vegetables you will grow. Look for plants that are ideal for your climate.
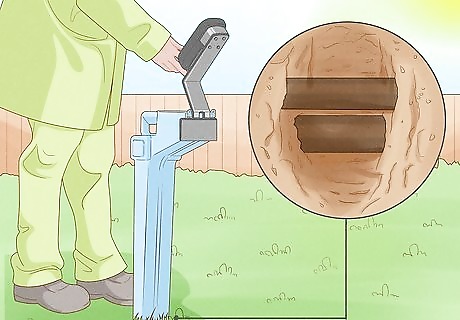
Check for buried utility lines. Once you have chosen a spot, make sure it can be used. It would not be fun to have your freshly planted garden dug up by your county. Look to see if there are any buried utility lines underneath the area. There should be a phone number available to check for the location of utility lines in your area. If not, call your local government to ask for the location of the utility lines. You should also ask about irrigation lines.
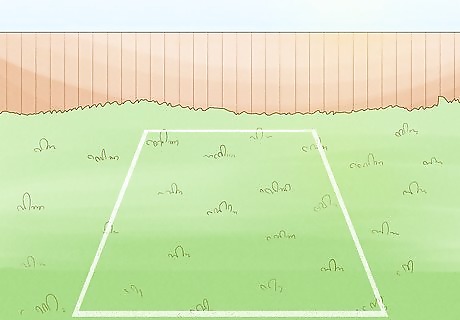
Mark off the area. Once you have made sure the area can be used, mark off the exact location of the bed. Spend some time planning the exact dimensions of your garden bed. Consider how much you will be planting, and how much space the plants will need. Then, go to your local hardware store and purchase paint that is made specifically for painting lines on the ground. Use the paint to mark of the location of the garden bed. You can also use cans of spray chalk, but paint usually holds up better with moisture.
Preparing the Soil
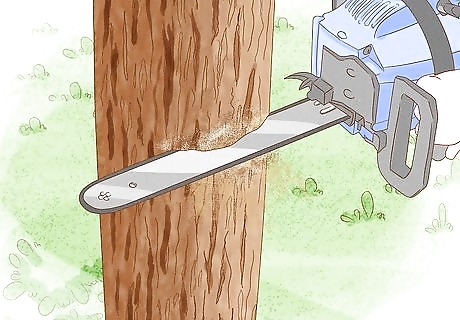
Kill existing vegetation. You will need to remove and then kill all of the existing vegetation in the area you have marked off. You should begin doing this during the fall and winter so that the bed is ready by spring. If you have woody material in the area, you will need to remove it with pruners or a chainsaw. Grass and chickweed are easier to handle because they can be mowed, though this will not remove their roots. Weeds can be pulled, but there are easier ways to take care of weeds. You can kill the weeds and any other existing vegetation with newspaper.
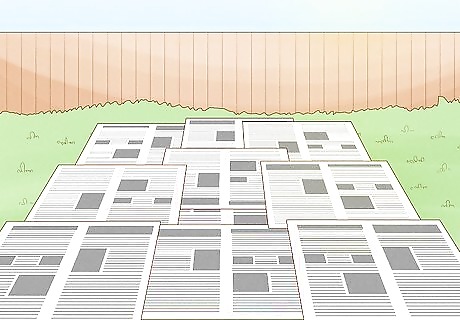
Cover the area in newspaper. To completely kill the existing vegetation, cover the marked off area in several layer of wet newspaper. The newspaper kills the vegetation by blocking out sunlight. Most newspaper ink should not be harmful to the soil, but make sure not use glossy, slick newspaper that is covered in advertisements. Cover the newspaper with a thick layer of compost. Leave the newspaper until spring. Depending on what you need to kill, this process may need to happen during the active growth seasons, that is, spring, summer and fall. Four or five sheets of newspaper should be enough.
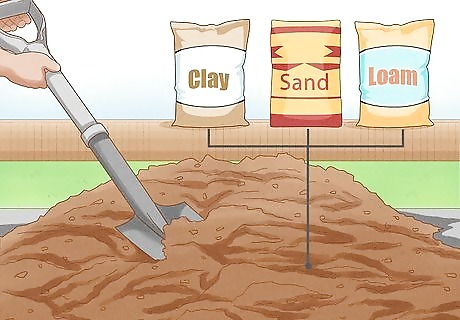
Assess the soil that you have to work with. You will need a combination of loam, sand, and clay. You should be able to squeeze your soil into a ball and then crumble it easily. Soil with too much clay will not crumble, and a soil with too much sand will not squeeze into a ball. To check your soil’s pH, you can test it on your own, or send in a sample to a laboratory.
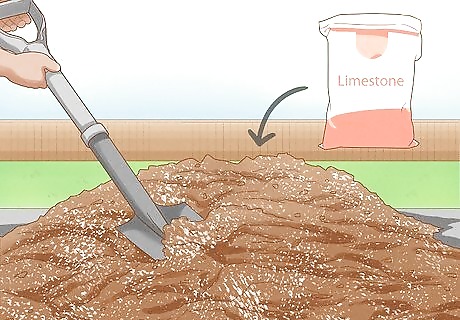
Adjust your soil’s pH. You can do this by adding a few inches of beneficial compost to your new vegetable garden. Most garden plants need acidic soil to thrive and adding compost or any organic material tends to increase acidity. Add the mix to the top of your garden a few inches deep, and then mix it into the existing soil. You can amend the acidity or alkalinity of soil by adding limestone or sulfur, depending on what results you are seeking.
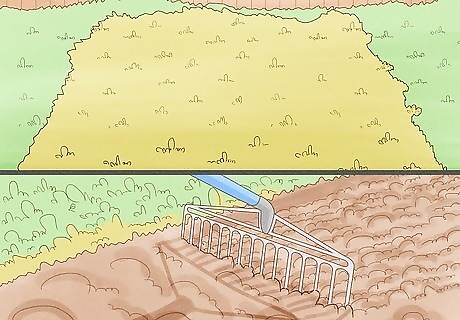
Turn the soil. Use a tiller, spade/shovel, or garden fork to turn the soil over. A spade or shovel may be the best to use for a very new and firm bed. The soil should be damp, but not wet when you are working with it. It should break apart, look moist, and not stick to your tools. If the soil is not moist, you can add water with a garden hose. Turn over about twelve inches of soil, though eighteen inches is ideal if you can dig that far. Soil that is too wet will clump when it is turned over. Soil that is too dry will be difficult to dig into.
Making the Bed
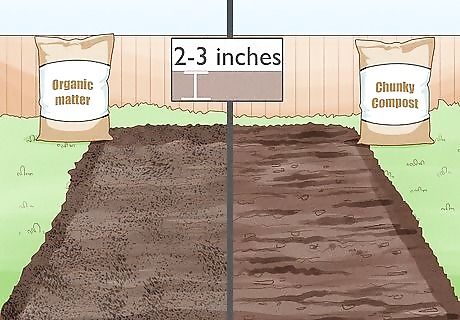
Fill the area in with organic matter. Once the bed has been turned, fill in the area with organic matter or compost. Spread two to three inches over the bed. Then, turn the soil again in order to mix the soil with the compost. Do not use compost that is too fine or has a sand-like consistency because it will break down too quickly. The ideal compost has chunks and small particles. Organic matter or compost is used to add nutrition and improve soil structure.
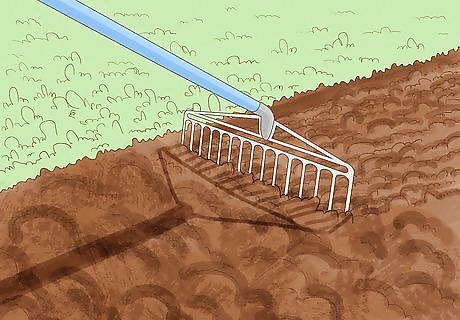
Rake the surface. Once you have added the compost, rake the area. Rake the surface until the soil is level. There shouldn’t be any large rocks or branches left in the soil.
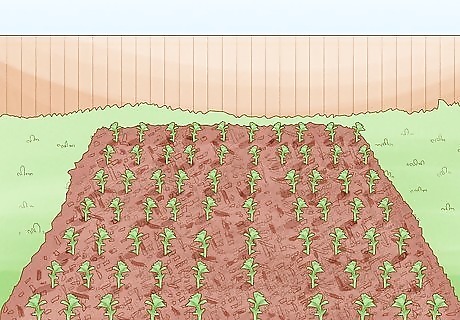
Apply a thick layer of mulch once the bed is planted. Once the bed is done and the garden is planted, you can add a layer of mulch or compost. This will keep the weeds from growing in your garden, and it will help the soil retain moisture. It will also keep the area looking neat.
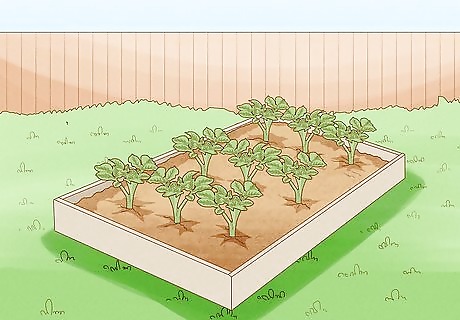
Opt for a raised bed if your soil will be difficult to maintain. If the bed doesn’t work out as planned, you can make a raised bed instead. This is a good option if your soil is too moist and heavy. A raised bed will allow the water to drain well. You can use a wooden border or rocks constructed a few inches high around the parameter of the garden so that the soil is packed securely inside. With a raised garden, you don't have to dig out the area and till the soil first.
















Comments
0 comment