views
- Put 2-3 drops of 3% hydrogen peroxide in your infected ear canal to help soften any buildup. Wait 10 minutes, then tilt your head and let the fluid drain out.
- Place a warm compress over the infected ear to relieve pain and increase blood flow (which leads to faster recovery).
- For a severe infection (excessive pain or fever) that won't clear up after 2-3 days, visit your doctor for a prescription solution.
Home Remedies
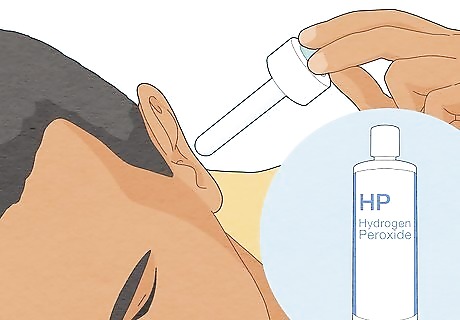
Apply 2-3 drops of 3% hydrogen peroxide using a medicine dropper. Let the drops sit in the infected ear canal for 5 to 10 minutes, then tilt your head to let it drain. 3% hydrogen peroxide will soften any crusted or hardened debris in the ear canal and help wash fungal colonies out of your ear. Consult a doctor before using hydrogen peroxide to treat your fungal ear infection.
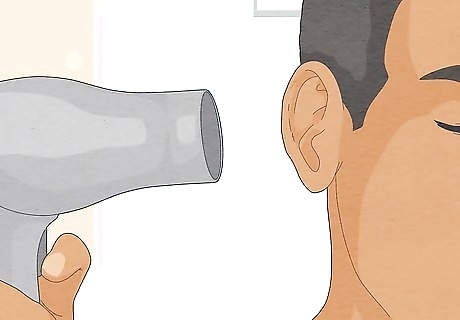
Use a hairdryer on low heat to dry any moisture in the ear canal. Turn your hairdryer to the lowest setting possible and place its end at least 10 inches (25.4 cm) away from the infected ear. This method will help to dry out any moisture in the ear canal and hinder fungus growth. Be careful not to burn yourself, and turn the dryer off if you feel discomfort.
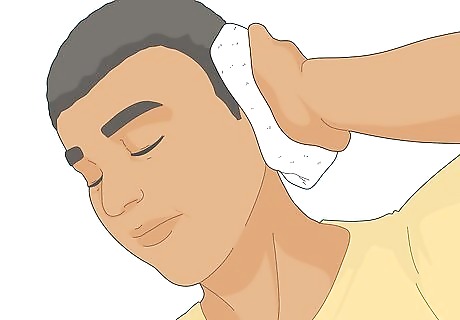
Apply a warm compress to the affected ear. Soak a clean washcloth in warm water, ensuring it’s not too hot. Then, place the washcloth over the infected ear and wait until it cools down. A warm compress will help relieve pain and inflammation without taking pain-relieving drugs. Plus, it increases blood flow to the infected area, which leads to faster recovery—yes, please! Alternate between a warm and cold compress every 10 minutes for extra pain-reliving power.
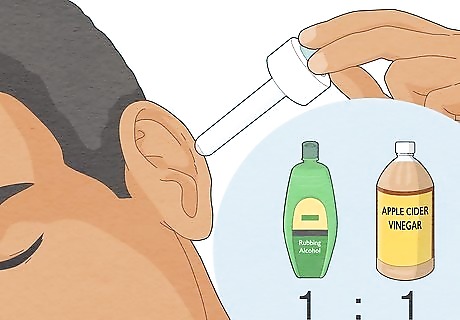
Use 2-3 drops of a 1:1 rubbing alcohol and apple cider vinegar solution. Mix a 1:1 ratio of rubbing alcohol and apple cider vinegar in a dropper. Then, add 2-3 drops of the solution to the infected ear. Let the drops sit in your ear for 10 minutes, and tilt your head to let it drain. Re-apply this mixture every 4 hours for up to 2 weeks. Rubbing alcohol is a disinfectant and a drying agent that helps remove the moisture in the ear canal, causing your fungal infection. The acidity of the apple cider vinegar slows the growth of the fungus, as Candida and Aspergillus fungus strains prefer a "basic" environment for optimal growth.
Eat foods rich in vitamin C, like citrus fruit. Vitamin C helps repair the damaged tissues in your ear by aiding the body in producing collagen, a powerful skin-repairing protein. Doctors recommend taking a 500 to 1,000 mg vitamin C supplement per day with food. Excellent dietary sources of vitamin C include citrus fruit (oranges, limes, lemons), berries (blueberries, cranberries, strawberries, raspberries), pineapples, watermelon, papaya, broccoli, spinach, Brussel sprouts, cabbage, and cauliflower.

Use 2-3 drops of garlic oil to help fight the fungus. Garlic oil is an effective antifungal agent in eradicating Aspergillus fungus (1 of the 2 main causes of fungal ear infections). Take a garlic oil capsule, puncture it, and pour it into the infected ear. Let it sit for 10 minutes, then tilt your head to drain the oil, and repeat the process daily for up to 2 weeks. Research suggests that garlic oil is just as effective at curing fungal ear infections as prescription medications.
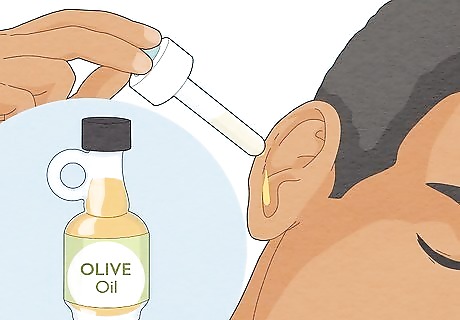
Use 3 drops of warm olive oil to help soften any blockages. If you have a fungal infection, there will be whitish or yellowish secretions from the ear and an overproduction of wax. All this buildup can cause blockage in the eustachian tube, and warm olive oil is the perfect way to soften it right up! Heat a small dish of olive oil in the microwave for a few seconds. Then, add 3 drops of the warmed olive oil to the infected ear using a medicine dropper. Let the drops sit in the ear canal for 5-10 minutes, then tilt your head to let it drain. Warm olive oil will soften earwax (cerumen) and any other hardened secretions in the ear canal, making them easier to remove. Olive oil has anti-inflammatory properties that help relieve the swelling and pain associated with fungal ear infections. Add 2-3 drops of tea tree oil to the warm olive oil in your medicine dropper and let sit it in your ear for 3 minutes for extra fungus-fighting power. Tea tree oil is a powerful antifungal that will help kill the fungal colonies in your ear.
Medications
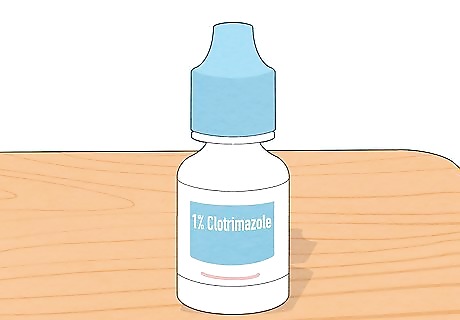
Use antifungal ear drops. 1% clotrimazole is the most popular antifungal medicine doctors prescribe to treat fungal ear infections. It kills both Candida and Aspergillus strains of fungal bacteria by inhibiting the enzyme that converts ergosterol, which the fungus needs to grow—infection be gone! Side effects include irritation, burning, or discomfort. Use clotrimazole by doing the following: Wash your hands with running water and mild soap. Then, clean the ear with warm water and a cotton swab until any visible secretions are gone, and gently pat the ear dry with a clean cloth. Lie down or tilt your head sideways to expose the ear canal and pull your earlobe downward, then backward. Apply 3 drops of clotrimazole into your ear, keeping your ear tilted for 2-3 minutes to allow the solution to reach the infected area. Then, tip your head, pouring out the medicine into a napkin. Store the medication away from children in a cool, dry place. If clotrimazole doesn’t get rid of your ear infection, your doctor may prescribe a different antifungal agent, such as miconazole.

Get a prescription for fluconazole (Diflucan). Your doctor may prescribe fluconazole if your fungal ear infection is severe. Fluconazole works similarly to clotrimazole, inhibiting the fungus from growing further. The most common side effects are a headache, nausea, dizziness, change in taste, loose stools, abdominal pain, skin rash, and elevation of liver enzymes. Fluconazole is taken in tablet form. Doctors normally prescribe 1 dose of 200mg once daily, then 100mg daily for 3-5 days.
Don’t take antibiotics. Antibiotics are only effective in treating bacterial infections, so they won’t help to combat your fungal ear infection. Plus, antibiotics can make the infection worse by killing the good bacteria residing in the ear or other parts of the body, which your immune system needs to help fight the infection off.Warning: Misuse of antibiotics can cause pathogenic bacteria to become resistant. Therefore, you should use them only when prescribed by a physician and strictly according to the indications.
See a doctor if you have intense pain, fever, or hearing loss. When you have an ear infection, it is best to visit your doctor to get an accurate diagnosis and determine the best course of treatment. If you’re experiencing intense pain, losing your ability to hear, have a fever, or drainage from the ear, seek professional help. Your doctor can clean your ear canal thoroughly with a suction device and provide medications to treat your ear infection. Your doctor may also recommend over-the-counter medications for pain or prescribe medication if the pain is severe.

Follow up with your physician after a week of treatment. See your physician again in a week or so to check that their prescribed treatment cleared up your cumbersome fungal ear infection. If not, your doctor may try a different approach if the treatment isn’t working as it should. Don’t worry—your doctor will get you feeling better soon! Call your physician if your symptoms worsen or do not improve within the first week of treatment.
Symptoms

Pay attention to abnormal ear itching (pruritis). While it’s normal for your ear to itch slightly now and then, you might have a fungal infection if your ear itches constantly and scratching/rubbing doesn’t provide much relief. Believe it or not, excessive itchiness in your ear canal is the primary way to identify an ear infection caused by fungus.
Watch out for ear pain (otalgia). Those suffering from a fungal ear infection have described the sensation as “pressure” or “fullness” in 1 ear. The pain can be mild or severe and usually intensifies the more you touch your ear.
Examine your ear discharge (otorrhea). Fungal ear discharge is usually thick and can be clear, white, yellow, or bloody/foul-smelling. Take a cotton swab and swab your ear (being careful not to insert the tip into your ear canal). You may have a fungal ear infection if the amount or color seems off (not the usual orangey-brown).
Check for hearing loss. A fungal ear infection can cause muffled speech/sounds, difficulty understanding words, and trouble hearing consonants. Sometimes, people recognize their hearing loss through a change in behavior, notably frustration. If you find yourself withdrawing from conversations and social settings due to an inability or difficulty to hear, you may be suffering from a fungal ear infection.
















Comments
0 comment