views
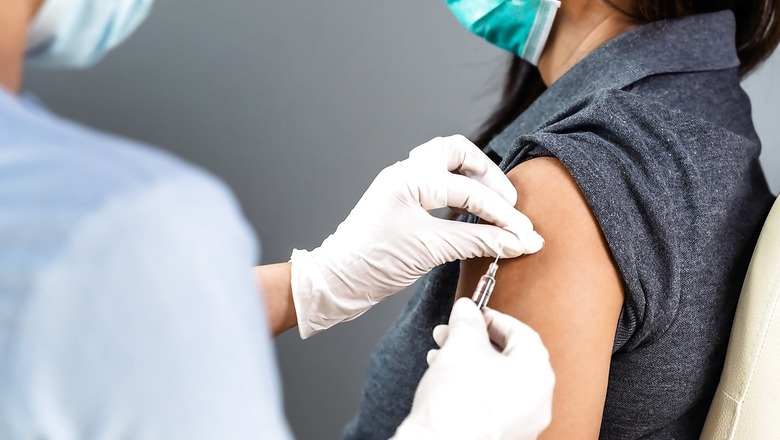
While India is facing the second wave of Covid-19, the government is trying its best to vaccinate the population as soon as people. Covid-19 vaccines are administered to the upper arm. If you are wondering why is that, here is your answer.
Why are Covid-19 vaccines injected into the upper arm only?
Most of the vaccines are injected in muscles only as the muscle tissue contains important immune cells that recognize the antigen. The antigen is a tiny piece of a virus or bacteria that stimulates an immune response. However, the Covid-19 vaccine does not introduce antigen but rather administers the blueprint for producing antigens. Hence it is administered to a thick, triangular shoulder muscle. It is also said to be less painful to get injected into the upper arms.
Also, muscles keep the action or reactions of vaccines localized.
How does the Covid-19 vaccine function?
Once the vaccine is injected into the upper arm, the antigens produced by it get carried out by immune cells to a nearby lymph node. Lymph nodes are key components of our immune system that contain more immune cells and hence start the immune process of creating antibodies. These special cells also teach the white blood cells, known as T cells and B cells, to either become killer cells, which seek out and destroy coronavirus-infected cells or antibody-secreting cells.
Most of the vaccines are administered to the area close to the clusters of lymph nodes. For instance, many vaccines are injected into the deltoid that is a thick, triangular shoulder muscle as it is close to lymph nodes located just under the armpit. When vaccines are given in the anterolateral (front) aspect of the thigh, the lymph vessels don’t have to travel far to reach the cluster of lymph nodes located in the groin.
Read all the Latest News, Breaking News and Coronavirus News here. Follow us on Facebook, Twitter and Telegram.
















Comments
0 comment