views
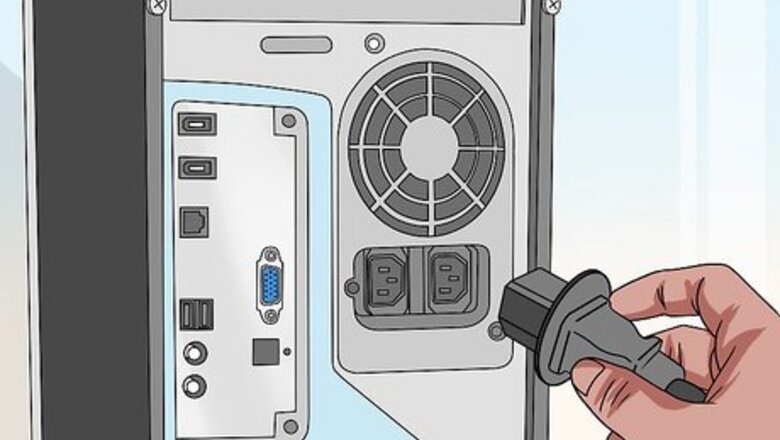
Check all wired connections.
Make sure your wires are plugged in properly. Check for any loose connections on your computer and monitor, and make sure they're securely fitted. If your computer has a dedicated graphics card (non-integrated), make sure you're plugging your monitor into the HDMI or DisplayPort of the actual graphics card. The location will be different from the ports on your computer's motherboard.
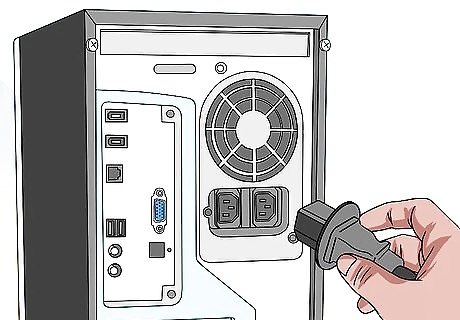
Try a different cable.
Use a new cable. If the wires are plugged in properly, you may not see a display due to a damaged wire. Try using a newer cable. If your monitor has both HDMI and DisplayPort ports, try using the alternate port instead.
Check the monitor power.
Confirm your monitor has power. Most monitors have a light indicator when it's turned on. It may be green when first powered on and stay orange when it's in standby mode. If you don't see any light on your monitor, make sure you're using the correct power cord.
Check the monitor source.

Make sure you're using the correct input source. On most monitors, you can press a physical button to switch sources. Cycle through each source, allowing at least 30 seconds for the change to register.
Restart your graphics driver.
Press ⊞ Win+Ctrl+⇧ Shift+B. This will restart the graphics driver on your computer. If the screen turns on after using this keyboard, make sure to update your drivers.
Hard restart your computer.
Press and hold your computer's power button. This will force your computer to turn off. Wait 30 seconds, and then press it again to turn it on. Try to avoid turning off your computer this way more than necessary; it can cause issues with startup in the future.
Use a different monitor.
Try using another monitor or screen. If you're able to connect to the other monitor, the problem lies with your previous monitor rather than your computer.
Check all individual components.
If you built your PC, check the components. Make sure to ground yourself to avoid damaging your computer with electrostatic discharge. Double-check that each component is fitted properly and is in the correct position.
Test your power supply.
Purchase a power supply tester to check your PC. Your computer may still be off even if the fans and lights are working. Use a power supply tester to make sure your computer is fully powered on.
Disconnect all peripherals.
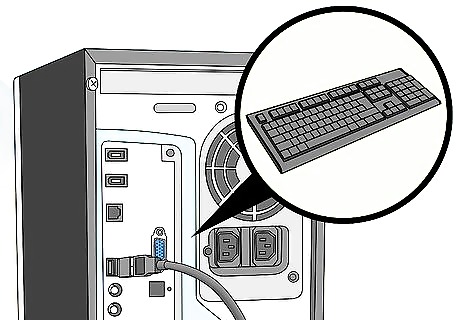
Temporarily unplug your keyboard, mouse, and other accessories. Restart your computer with just your monitor plugged in to make sure the problem isn't caused by other devices.
Open the BIOS.

Check your PC's performance and temperature in the BIOS. This will only work if you can see your screen sometimes. You can enter the BIOS by restarting your computer and pressing your manufacturer's designated key. Once you're in the BIOS, select the PC Health Status option. This may also look like System Hardware Monitor or similar. Make sure the CPU temperature is between 95-113℉ (35-45℃). If the temperature is above this optimal range, you may need to upgrade your components or move your PC to a different location.


















Comments
0 comment