
views
Using the Right Lure
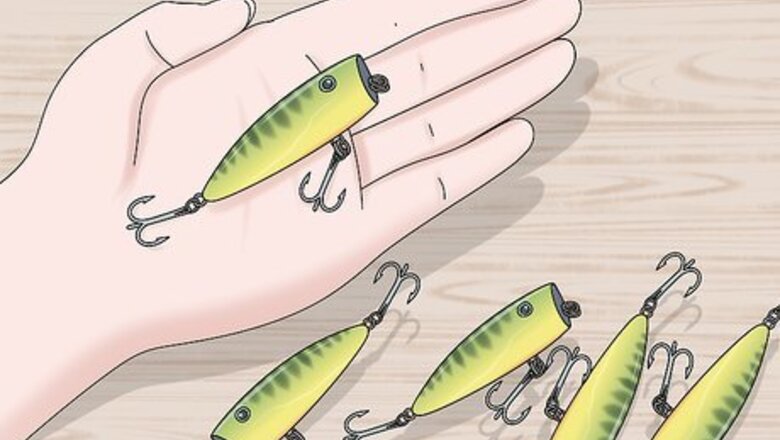
Choose a floating lure so you can see when a fish bites. Topwater, or floating lures, are the most popular and the easiest lures you can use. Their bright colors make them easier to see in the water and they’ll attract fish to them so all you have to do is cast them out and wait for fish to take the bait. Some floating lures, like the flies used in fly fishing, rest on the surface of the water. Floating lures are often lightweight so they don’t sink too far, which can make them difficult to cast long distances.Tip: You can use a bobber if you want to keep a lure floating near the surface of the water. You’ll also be able to see the bobber go under the surface of the water when a fish bites.

Go with a suspending lure to mimic a baitfish. Choose a suspending lure to entice larger fish by presenting them with what looks like an easy meal. A suspending lure hovers between the surface of the water and the bottom and acts as a baitfish to fool larger fish into eating it. Common suspending lures include crankbaits, slash baits, and jerk baits. Suspending lures are useful for catching freshwater fish such as bass, as well as saltwater fish such as redfish. Use a suspending lure in cold weather to attract slower moving fish.
Reel subsurface lures to you to attract larger fish. A subsurface lure floats just below the surface of the water and is meant to be continuously reeled in in order to resemble a fish moving through the water. The sound and movement of the lure through the water will attract larger fish to it. Reel in the lure at a steady, slow pace to make it look realistic to predatory fish. Many subsurface lures are designed to mimic injured baitfish, which makes them seem like an easy target for larger fish. You can catch both fresh and saltwater fish such as mullet, bass, redfish, and drum with subsurface lures.
Select a sinking lure to catch larger freshwater fish. Sinking lures, also known as jigs, begin to sink as soon as you cast them into the water. As you reel it in, the lure will stay at a lower level in the water, which is where larger fish are much more likely to be. Use sinking lures to catch large bass and other big freshwater fish.
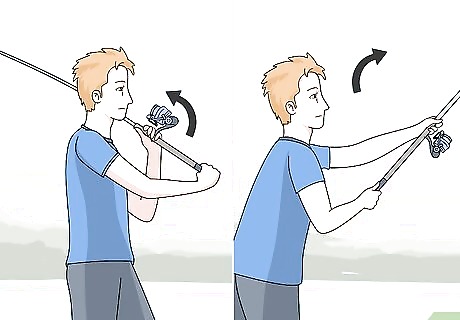
Cast your fishing line in an area likely to have fish. Hold the rod with your dominant hand and press the reel spool release button. Then, bring the rod up and back toward your shoulder and sweep it forward in front of you as you remove your thumb from the spool reel to cast your pole. When the lure lands in the water, turn the knob forward until it clicks to keep anymore line from coming out. Aim for an area where fish are swimming by or congregating so they’ll see your lure. When you’re casting your line, reel it in so your bait is hanging about 12 inches (30 cm) from the tip of the fishing rod. Look for areas with obstructions that fish will want to congregate next to such as logs, large rocks or structures, or small channels away from the moving water. Be careful not to accidentally hook onto any trees or shrubs behind you when you're casting your line.
Setting the Hook
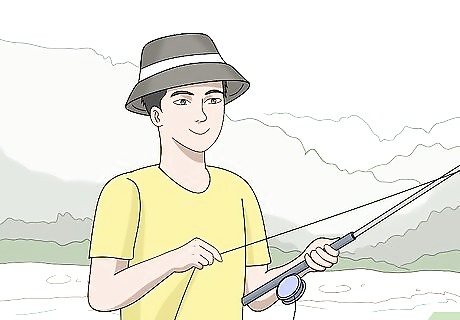
Reel in the slack so you can feel when a fish bites. Gently turn the knob on your reel to remove the slack from the fishing line. You will be able to feel the lure at the end of the line as it moves or floats through the water. A taut line will allow you to feel when a fish nibbles or bites so you can know when to set the hook. If your lure or bait moves in the water and the line slackens, reel it in gently to make the line taut again.
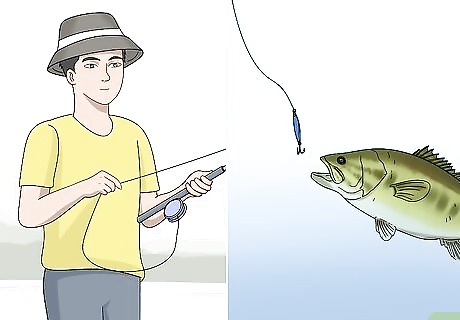
Keep your fishing pole still and allow the fish to nibble at your bait. Fish are easily startled by noise or sudden movements, so if you feel a fish begins to nibble at your lure, stop reeling in, and remain as motionless as you can to allow the fish to take the bait. Small bumps or nibbles may not be enough to successfully hook the fish, so don’t try to set your pole as soon as you feel a small bite.
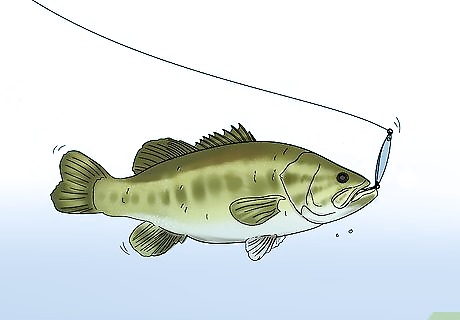
Wait until the fish begins to swim away with your bait. You’ll know a fish has really taken a bite of your lure when you see your line moving. Wait until you feel a strong tug and then look to see if your line is moving around for a sign that a fish has completely taken your bait. If you’re using a bobber, wait until you see the bobber go completely beneath the surface of the water.Tip: Some fish may be apprehensive about taking your bait and may test it by nibbling or bumping against it. Wait until you feel the constant pull of a fish on your line to set your hook.
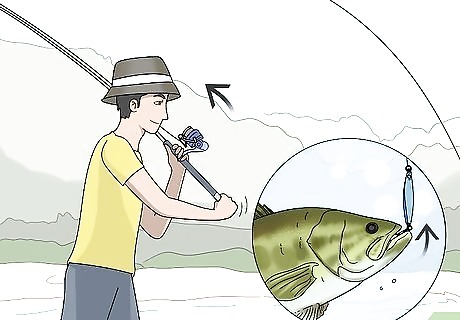
Snap the rod up into the air to set the hook in the mouth of the fish. As soon as you feel the big tug of a fish taking your bait on the line, jerk the rod up and back into the air. The hook will snag the lip of the fish and it will start to fight to get away. Start slowly reeling in the fish, but don’t strain the fishing line too much or it may break. Avoid setting the hook multiple times or you could pull it out of the mouth of the fish. Use 1 snapping motion to set the hook rather than multiple jerks.
Reeling in a Hooked Fish
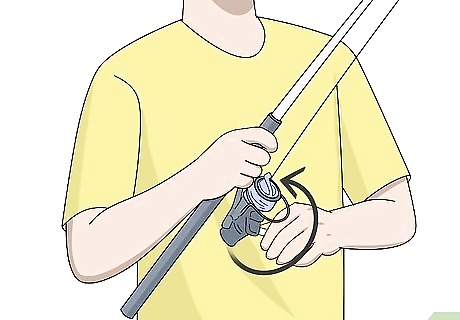
Keep the tip of your fishing rod up as you reel. Avoid cranking the pole and reeling the fish in as fast as you can or you could pop your line or lose the fish. Instead, allow the fish to tire itself out as you keep your fishing pole held up. Move the pole from side to side to allow the line to follow the fish so it doesn’t build up too much tension. Keeping the rod at about a 45-degree angle with the tip pointed up keeps the line from dragging too much.

Make sure the line stays tight so the fish can’t escape. Keep the line taut as you’re fighting the fish. Reel in any slack that’s created by the fish moving through the water. A loose line could cause the hook to slip out of the mouth of the fish and allow it to get away. Don’t strain the line or it could break. Allow the fish to fight until it tires itself out and starts to build up slack in the line that you can easily reel in.

Bring the fish in close enough to you to grab out of the water. In time, the fish will tire out and it will become easier for you to reel it in. Continue reeling the fish until it’s close enough for you to reach down and grab the line. When the fish is close enough for you to see it, check to see if it looks tired and is rolled over on its side. It will be easier to take out of the water.Tip: If you’re fishing from a boat, be careful not to let the fish get underneath you or the line could break over the side of the boat.
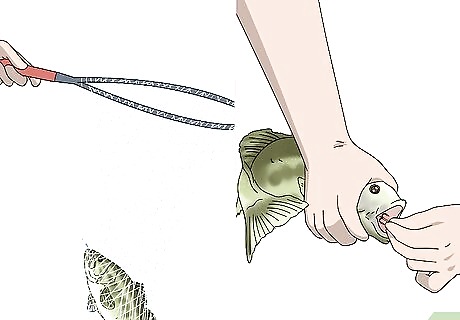
Grab the line to pull the fish out of the water. Reach down and take a firm hold of the fishing line just above the water. Use 1 smooth motion to pull the fish from the water. The fish will likely continue to jerk and fight, so quickly place it into a net, in the boat, or on the land away from the water so it can’t escape. Hold the fish down with 1 hand and use the other to pull the hook from its mouth. If you aren’t planning to keep the fish, gently release it back into the water after you remove the hook.

















Comments
0 comment