
views
X
Research source
Because the grammar and structure are so different, learning Pashto can be difficult for native English speakers. However, with practice, you can succeed at learning Pashto. Study diligently and have patience. Kha kismet darta ghowaram! (Good luck!)
Understanding Pronunciation and Structure

Practice pronouncing the Pashto alphabet. If you can learn to pronounce the letters of the alphabet, you'll be able to sound out words you see (even if you don't know what they mean). Drilling pronunciation can also help you learn the script. Many letters in Pashto are pronounced using different parts of your mouth and tongue, much like other Indo-Iranian languages. However, Pashto also has many sounds in common with Indo-Aryan languages (such as Sanskrit). For example, Pashto has retroflex consonants, which you pronounce by curling your tongue so that the back tip of your tongue touches the roof of your mouth. A video lesson on pronouncing the Pashto alphabet is available at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y5QZE9ew6eg. Indiana University also has a printable PDF of Pashto alphabet pronunciation available at https://iaunrc.indiana.edu/documents/languages/Pashto_Alphabet.pdf.

Pay attention to the stress in words. In Pashto, the syllable stressed is not uniform. Stress can fall on any syllable of the word, and often is used to distinguish meanings between words that would otherwise be identical. For example, the word áspa (with stress on the first syllable) means "mare," while the word aspá (stress on the last syllable) means "spotted fever." You wouldn't want to get these confused if you were bartering with a local for a horse to ride through the countryside.

Put the object before the verb. Particularly if you speak English or another European language, normal word order in Pashto sentences may give you some trouble. Typically, Pashto sentences follow subject-object-verb word order. For example, the Pashto word for "dai" is the Pashto word for "is." If you wanted to say "this is a book," you would say "Dā Ketāb dai." Look at the word order – dai comes last. You're literally saying "This book is." Other Indo-Aryan and Indo-Iranian languages use this order, as well as some Asian languages. If you are familiar with any of those, this particular aspect of Pashto probably won't be a problem for you.

Change verbs and nouns to suit the context of the sentence. While there are no articles in Pashto, nouns are highly modified to reflect gender, number, and case. Verbs are modified to indicate tense, voice, aspect, and mood. In Pashto, the aspect (perfect, meaning it is a complete action, or imperfect, meaning it is a progressive or continuous action) is as important as tense.

Read Pashto script from right to left. As with Arabic and many other Indo-Iranian languages, Pashto is read right to left, rather than left to right as English and other European languages are. If you're not familiar with other languages that read this way, it can take some getting used to. When you start practicing script and writing the alphabet, get in the habit of starting on the right side of your page and moving left, rather than the other way around. If you're writing, it can also help to invest in notebooks that are bound on the right side rather than the left.
Saying Simple Phrases
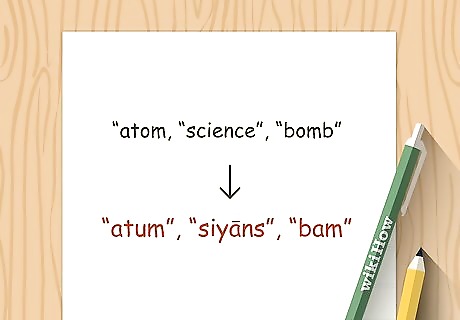
Recognize borrowed words. Pashto shares an extensive vocabulary with other Indo-Iranian languages, Urdu, and Arabic (due to the influence of Islam on Pashtun cultures). If you know any of these languages, you likely already know how to say a number of words in Pashto. When talking about science, technology, politics, and the military, you will also encounter many words that are borrowed from English, including words such as atum (atom), siyāns (science), and bam (bomb). Pashto even has words borrowed from Greek, owing to the Greek occupation in the 3rd century BC of present-day Afghanistan. The task of memorizing every word is simply too daunting and sometimes counterproductive for both beginners and advanced learners. Try to tackle 20-50 words per lesson, day, or week. Work on the most essential and general words first, then move on to the more specific ones.

Greet others by saying "as-salaamu' alaykum" (ah sa-LAAM-uu ah-LEH-kum). This greeting is a standard Arabic greeting common among Muslims, which literally means "peace be upon you." The phrase has been imported into Pashto and is commonly used in place of "hello." "Khe chare" (KHE chaa-reh) is a more informal way of saying "hello," similar to "hi" or "hey" in English. If someone says "as-salaamu' alaykum" to you, the proper response is "walaykum salaam" (wa-LEH-kum sa-laam), which essentially means "and also with you."

Say "Ta sanga yee?" (TSENG-ga yeh) to ask "How are you?" After you've greeted someone, it's typically natural to ask this question. If they ask you first, you can reply "Za kha yam, mannana, ta sanga yee?" (za KHE yem, ma-NE-na, TSENG-ga yeh) This essentially means "I'm doing well, and you?" You can also say "k'he yem, manena," which means "fine, thank you."

Ask someone's name by saying "staa num tsa dhe" (STAA noom TSE dai). Once the initial greetings are over, you likely want to know who you're talking with, as well as properly introduce yourself. Use the phrase "zama num" followed by your name, then the word "de" to tell them your name. Once the person has introduced themselves, you can say "khushala shum pa li do di," which means "pleased to meet you."

Let the person know you only know a little Pashto. Once the initial greetings are out of the way, you likely want to let your conversation partner know that you don't actually speak Pashto very well. Say "ze pe puk'hto samē khaberē ne shem kawulay," which means "I can't speak Pashto well." If they ask if you speak Pashto ("Aya ta pa pakhto khabarey kawalai shey?"), you might reply "lag lag," which means "Yes, a little." If your pronunciation of the initial greetings was strong, the person might start speaking to you in rapid-fire Pashto. You can interject "za na poheegum," which means "I don't understand," and then slow them down by saying "karaar karaar khabaree kawa" (please speak more slowly).
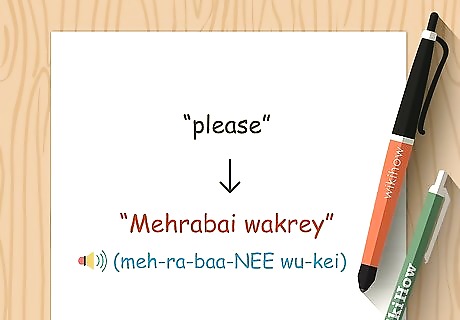
Mind your manners with polite words and phrases. Saying please and thank you will go a long way when you are just learning Pashto and trying to converse with native speakers or navigate an area where the language is spoken. "Mehrabai wakrey" (meh-ra-baa-NEE wu-kei) is "please" in Pashto. You can also say "lotfan." For "thank you," you can say either "manana" or "tashakor." If someone says one of these words to you, reply "har kala rasha," which essentially means "any time." For "excuse me" or "I'm sorry," say "bakhena ghwaarum"(ba-KHE-na ghwaa-rrem).
Using Free Online Resources

Access resources from the Defense Language Institute. The US Department of Defense runs the Defense Language Institute Foreign Language Center. The website hosts numerous materials for learning Pashto, which you can search through at https://www.dliflc.edu/about/languages-at-dliflc/. While these resources are primarily geared towards military personnel stationed in regions where Pashto is spoken, there are also introductory materials that are appropriate for any beginner. You will also find resources that can familiarize you with the culture and traditions in areas where Pashto is spoken. Understanding the culture may help you understand the language better.

Use the CeLCAR modules. Indiana University has online Pashto lessons available for free at https://celcar.indiana.edu/current-projects/online-language-courses/online-language-pashto.html. To take the lessons, you must first register for a free account. There are 10 modules that include audio and text, as well as some exercises.

Watch news stories from Afghanistan online. The Afghanistan television network Ashna has a YouTube channel where you can watch hundreds of short news videos in Pashto to practice your comprehension as well as learn about issues of importance in the region. To watch or subscribe to the channel, go to https://www.youtube.com/user/VOAAFGHANISTAN. You can also scroll related channels to find other YouTube channels in Pashto you can watch for free.

Try the Beginning Pashto textbook to learn Pashto script. The US Department of Education's Center for Applied Linguistics created an introductory textbook for teaching both oral and written Afghan Pashto. This textbook is available online for free at https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED364085.pdf. While the textbook is somewhat dated, it can help you get a grasp on the basics of Pashto script, which hasn't changed since the textbook was last revised in 1993. The textbook also includes dialogues and readings, vocabulary, and grammar lessons. You can download the audio files that are meant to accompany the textbook for free at https://web.archive.org/web/20061212195024/languagelab.bh.indiana.edu/pashto.html.

Participate in Pashto language forums. There are numerous forums and social media networks online that you can use to read, watch videos, and talk to native speakers and fellow students alike. There is also a Pashtun forum on Reddit at https://www.reddit.com/r/Pashtun/. Many of these posts are in English and relate to news and information about areas where Pashto is spoken, but there are also posts and conversations in Pashto. Native speaking people and more advanced and experienced learners are always willing to help on different language forums. You can also benefit from other people’s questions and responses.

















Comments
0 comment