views
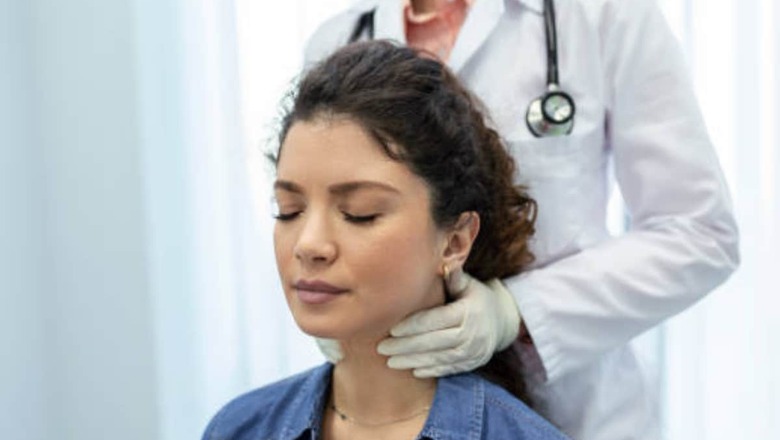
Lymphoma is a type of cancer that affects the lymphatic system, a vital part of the body’s immune system. While it may not be as widely discussed as other cancers, it’s crucial to raise awareness about this condition to promote early detection and improve outcomes.
Dr Prashant Mehta, Senior consultant, Dept of Medical Oncology and BMT, Amrita Hospital, Faridabad, says, “Lymphoma is a type of blood cancer that originates in the lymphoid organs, such as lymph nodes (small structures within different parts of the body, like the neck, armpit, groin, abdomen, and chest, which filter infectious organisms, cancer cells, and foreign substances), spleen, liver, and tonsils. Lymphoma generally cannot be detected in a blood examination unless it is very advanced or of the indolent variety.”
Types of Lymphoma
Dr Sameer A. Tulpule Consultant, general haematology, haemato-oncology and bone marrow transplantation, Kokilaben Dhirbhai Ambani Hospital Mumbai explains lymphoma is a cancer that originates in the lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell. It can be broadly categorized into two main types: Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Both types involve abnormal cell growth in the lymph nodes, spleen, and other lymphatic tissues.
Causes of Lymphoma
Dr Tulpule explains the causes of lymphoma:
- Genetic Factors: Some genetic mutations can increase the risk of developing lymphoma.
- Immune System Compromises: Conditions that weaken the immune system, such as HIV/AIDS, can make individuals more susceptible.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain chemicals and pesticides may be linked to lymphoma.
- Viral Infections: Infections like Epstein-Barr virus have been associated with an increased risk of lymphoma.
Symptoms of Lymphoma
“Aggressive lymphomas (DLBCL, Burkitt) present with rapidly enlarging swellings in the body (generally in the neck, armpit, groin, and abdomen), fever, night sweats, weight loss, facial swelling, cough, tonsillar enlargement, an enlarged spleen, and in later stages (when bone marrow becomes involved), low blood counts like anemia, low platelet, and low white cell count. These can be fatal without treatment but are mostly curable,” adds Dr Mehta.
Slow, indolent lymphomas like follicular lymphoma, lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma, and marginal zone lymphoma can remain without symptoms for long periods before requiring treatment. Dr Mehta believes, “Slow lymphomas can rarely transform into aggressive lymphomas, making them difficult to cure. Slow lymphomas are associated with a long lifespan but are generally not considered curable. Lymphomas can also present like leukemia (leukemic phase) and can be visualized in the blood when they involve the bone marrow.”
Dr Tulpule shares the effects of Lymphoma
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: An early symptom is often painless swelling of lymph nodes.
- Fatigue: Lymphoma can lead to fatigue, weakness, and weight loss.
- Night Sweats and Fever: These symptoms are common in lymphoma patients.
Treatment
Lymphoma treatment varies based on type and stage but often includes chemotherapy, radiation, and targeted therapies. Advances in immunotherapy and cellular therapy eg CAR-T cell therapy are highly effective options.
Outcomes vary; early detection and treatment yield better results. Many patients achieve remission, but long-term effects and relapses can occur, emphasizing the importance of ongoing care and monitoring.
“Newer therapies like CAR T-cell therapy (genetically modified T lymphocytes) and BiTEs (Bispecific T cell engagers) are also now available for patients whose disease does not respond to conventional therapy and initial treatment or is refractory,” opines Dr Mehta.
Although lymphoma is mostly a sporadic (randomly occurring) disease, and a few risk factors may be non-modifiable, there are a few lifestyle changes that could reduce the risk of getting lymphoma and cancer in general.
Maintaining a healthy weight, exercising, and avoiding tobacco and smoking can reduce the risk of lymphoma. Some autoimmune conditions can increase the risk of lymphoma; stress can cause flares of such conditions, so it is recommended to avoid stress. A balanced hygienic diet is similarly beneficial in reducing the risk. Certain types of breast implants can rarely lead to lymphoma, so women with implants need to be aware of this. Patients on immunosuppressants after kidney or liver transplant should make sure they follow the advice of their doctors carefully to avoid increased risks and get early diagnosis. Some viral infections like hepatitis C and HIV can substantially increase the risk of lymphoma, so to reduce your risk of acquiring these viruses, engage in safe sexual practices. People who have persistent heartburn-type symptoms may be harboring a hidden H. pylori bacterial infection, which can increase the risk of a specific type of lymphoma. Exposure to ionizing radiation, some chemicals, and pesticides can increase the risk, so unnecessary exposure must be avoided.
“Awareness about lymphoma is essential for early diagnosis and effective treatment. While the exact causes of lymphoma may not always be clear, understanding risk factors and recognizing symptoms can lead to better outcomes for those affected by this cancer. Regular check-ups and a healthy lifestyle are crucial for reducing the risk of lymphoma and improving overall health. It is advised to visit your nearest doctor or multispecialty hospital with full time speciality services to avoid delay in early detection,” signs off Dr Tulpule.


















Comments
0 comment