views
- To go to a website by address, start by opening a web browser on any device.
- In the browser's address bar, type the URL you want to go to, like https://www.wikihow.com.
- If you visit a specific page frequently, your browser will remember it and suggest it whenever you type the same address.
Using the Address Bar
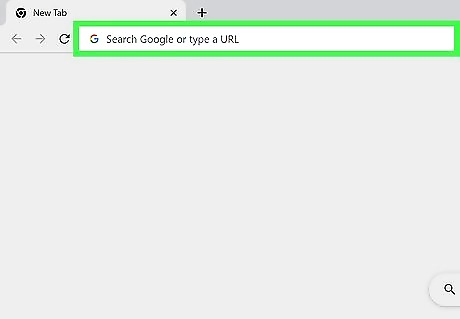
Type the website address you want to visit in the address bar. It's at the top of your screen. You'll see the address bar at the top of the page unless you're using iOS, which shows the address bar at the bottom of your screen. For example, the website could be www.wikihow.com, irs.gov, or amazon.co.uk. You can skip entering https:// for most websites, but you want to enter .com, .co, or whatever the ending is.

Press ↵ Enter or ⏎ Return on your keyboard. If you're on a phone or tablet, tap the "Go" or "Enter" button on the on-screen keyboard. You'll go to that website. You might see an error page if you didn't type the address correctly. In that case, you can enter a part of the website you remember and follow links to the specific page. Or you can simply search for the specific page, like "Facebook login." If you're entering a longer URL, it might be easiest to copy and paste it into your address bar so you don't misspell it.
Website URL Basics
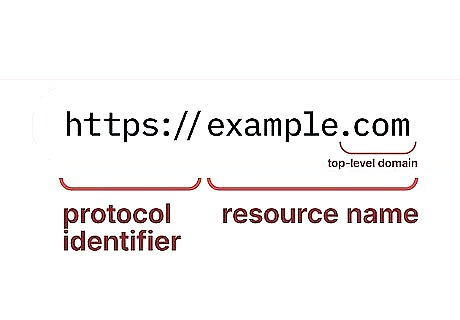
A more in-depth explanation of a web address. A website's address is also called a "URL," which stands for Uniform Resource Locator. A URL has two main parts: The protocol identifier and the resource name are separated by a colon and two forward slashes. Protocol identifier: The first part of a URL, which comes before the ://, indicates what protocol your web browser should use. For the URL https://example.com, the protocol identifier is https. https:// is the default for most pages, but some older pages will have http:// The "s" means information is secure and prevents the information from being intercepted, so "http://" websites aren't secure. Your browser may not show the "http" or "https" once the website loads. Resource name: This part of the address, which comes after ://, specifies the website's domain name or IP address—in other words, the path the browser needs to take to access the website. For the URL https://example.com, the resource name is example.com. example.com is a called a "domain name." Every domain name has a top-level domain, which is the part that comes after the dot—.com, .net, and co.uk are all top-level domains. Entering the addresses www.example.com and www.example.co.uk will take you to two different websites, so make sure you type the top-level domain exactly as it's written. Some top-level domains (e.g., .com, .org, and .net) are reserved for specific locations or industries. For example, .ca is reserved for Canadian websites, and .gov is reserved for United States government websites. The text that comes before the domain name, such as "www," is called a subdomain. The default subdomain is "www," so if you don't type that part, you usually won't get an error. However, sites can have subdomains other than "www," such as video.google.com. Make sure you include the subdomain if it is part of the URL.















Comments
0 comment