views
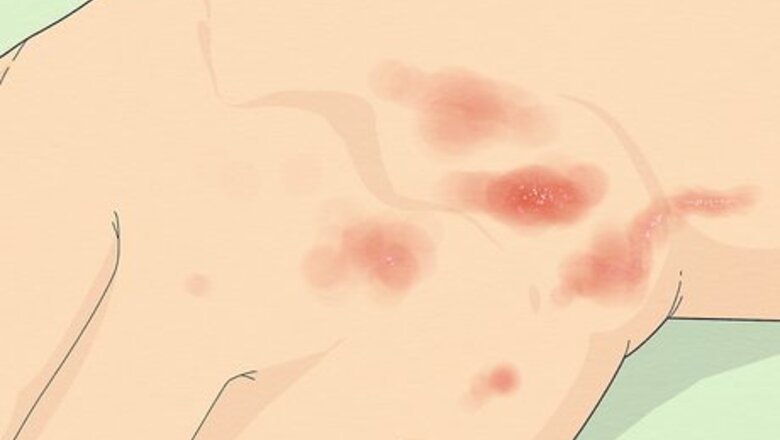
- Look for a bumpy, scaly red rash that forms a solid line. The bumps might look like hives or pimples.
- Watch for other symptoms of scabies, like intense itching, sores, and crusts on the skin.
- Make an appointment with your doctor to diagnose and treat scabies. Anti-itch creams and medications can help alleviate the symptoms.
- Avoid getting scabies again by staying away from people who are actively infected.
Symptoms

Bumpy and scaly red rash The most common symptom of scabies is a bumpy red rash that often forms a solid line. The bumps that form the rash might look like hives, pimples, or scaly patches that resemble eczema. The most common places you might see a scabies rash include: Hands, especially between the fingers and around nail beds Arms, especially around the elbows and wrists Anywhere covered by clothing, like the glutes, waistline, genitals, or nipples
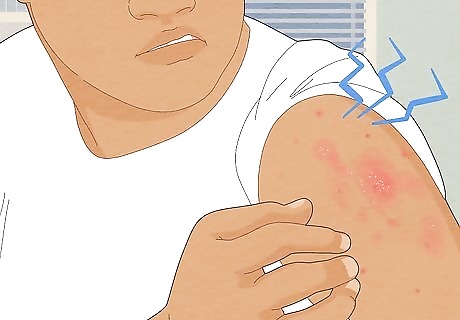
Intense itching, mainly at night Itching is caused by small mites burrowing underneath the skin and leaving behind eggs and waste. This itching can be so intense that it keeps the person up at night. In children, itching can be so intense that it causes them to cry.
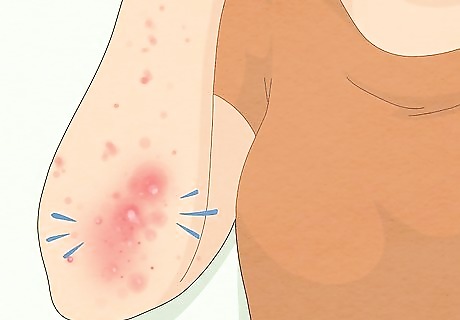
Sores on the skin A scabies rash usually leads to itching, and that itching can cause sores to develop on the skin. Unfortunately, these sores are prone to infection, which can lead to oozing. Signs of infection include increased redness, swelling, pain, or pus or discharge from the sores. If you believe your rash is infected, call your doctor right away. Your doctor can prescribe an oral or topical antibiotic to treat the infection. These bacteria can also lead to inflammation of the kidneys and sometimes sepsis, which is a life-threatening bacterial infection of the blood. If you have symptoms like a fever, chills, or vomiting, visit your doctor to have them diagnose you with sepsis. To avoid this, try to be gentle on your skin and do not scratch it. If you can't help yourself, consider wearing mittens or wrapping your fingertips with band-aids to keep yourself from damaging the skin.

Crusts on the skin Crusted scabies, also known as Norwegian scabies, is a severe form of the infestation. It is characterized by tiny blisters and thick skin crusting that can cover large areas of the body. Crusted scabies primarily occurs in individuals with weakened immune systems, because the impaired immune response allows mites to reproduce unchecked. Another consequence of the impaired immune response is that itching and the rash may be less severe or totally absent. This is because itching and a rash are immune responses, which may not happen in a weakened immune system. You are at risk for the development of crusted scabies if you are elderly, have a weakened immune system, or are living with HIV/AIDS, lymphoma, or leukemia. You are also at risk if you have received an organ transplant and have any condition that may prevent you from itching or scratching, such as a spinal cord injury, paralysis, or loss of sensation.
Diagnosis

Make an appointment with your doctor for a diagnosis. Your physician will diagnose scabies by examining you for the scabies rash and mite burrows. They will likely use a needle to scrape off a very small piece of skin. The doctor will then examine the matter under the microscope to confirm the presence of mites, eggs, or mite fecal matter. Keep in mind that you can still be infested with scabies even if mites, eggs, or fecal matter cannot be found. An infestation of scabies averages 10 to 15 mites found over the entire body.
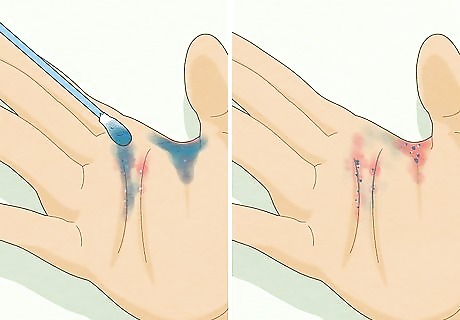
Get a burrow ink test to confirm your diagnosis. Your doctor can use an ink test to identify the burrows of scabies mites. Your doctor will rub ink around an area of skin that is itchy or irritated and then use an alcohol pad to wipe off the ink. If a mite burrow is present in your skin, it will trap some of the ink and the burrow will show up as a dark, wavy line on your skin.
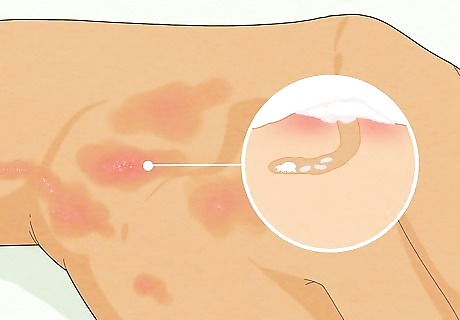
Rule out other skin conditions with your doctor. There are numerous other skin conditions that may be confused with scabies. The main way to distinguish them is through the mite burrows, which are not associated with any of the skin conditions that may be confused with scabies. Ask your doctor to rule out these other conditions so you can be sure you have scabies. Scabies is sometimes confused with other insect bites or stings, like bed bugs. You can identify bed bug bites by looking for red, raised bites in groups of three. It can also be confused with eczema, which is a chronic skin condition involving inflammation of the skin. The red pimple-like rash of eczema represents an allergic reaction. People with eczema can also get scabies, and the condition is typically more severe for them. You could also have folliculitis, which is an inflammation, and usually infection, in the area associated with a hair follicle. This conditions causes small white-headed pimples to crop up on a reddened base around or near hair follicles. It may be confused with psoriasis as well. Psoriasis is diagnosed by excessive growth of skin cells that leads to the formation of thick, silvery scales and itchy, dry, red patches.
Treatment
Permethrin There are currently no over the counter medications to treat scabies, but your doctor may prescribe you permethrin 5% cream to kill mites and eggs. Treatment for scabies involves getting rid of the infestation with prescription medications, which are called scabicides because they kill the mites. To use this cream, apply it from the neck down over your entire body, then wash it off after 8 to 14 hours. After 1 treatment, wait 7 days, then do a second treatment. This cream may cause stinging or itching, which are normal side effects. Talk to your doctor or pediatrician about treating infants and young children with scabies. Permethrin cream is safe for infants as young as 1 month old, but most experts recommend also applying it to the head and neck area for infants and young children.

Crotamiton 10% cream This cream is another scabicide that your doctor may recommend. To use it, apply it from the neck down over the entire body after a bath. Apply a second dose 24 hours after the initial dose and bathe 48 hours after the second dose, and repeat both doses in 7 to 10 days. Crotamiton is considered safe when used as directed. However, frequent treatment failure has been reported with this scabicide, which means it isn't the most effective or widely used anymore.

Lindane 1% lotion Similar to other scabicides, this lotion is prescription only. Apply the lotion from the neck down, and wash it off after 8 to 12 hours (after 6 hours for children). Repeat the treatment after 7 days to fully kill the scabies mites and eggs. Lindane is not safe for young children, women who are pregnant or nursing, or people with weakened immune systems. Since lindane is potentially neurotoxic, meaning it can cause damage to the brain or nervous system, it is typically saved for those who have been resistant to other treatments first.

Anti-itch cream Over the counter anti-itch creams and lotions, like Sarna or Aveeno anti-itch moisturizers, help reduce irritation. While you wait for your treatments to work, consider buying an OTC medication to stop the itching that comes with scabies. You can also try calamine lotion or 1% hydrocortisone cream.

Antihistamines Antihistamines are typically used as allergy medication, but they can help reduce swelling and irritation. Buy a bottle of antihistamines and follow the dosage instructions on the package to treat the symptoms of scabies. Talk to your doctor before giving antihistamines to a young child or infant.
Prevention

Avoid exposure with people who have scabies. The most common way that scabies is transmitted is via skin-to-skin contact. You can prevent scabies by staying away when you know someone is infected. In adults, scabies is often contracted through sexual activity, although it’s the skin-to-skin contact that does it, not the sex itself. Crowded conditions are a common cause for scabies outbreaks. Areas like prisons, barracks, child-care and elder-care facilities, and schools are common sites. Certain groups of people, like young children, mothers, sexually active adults, and residents of nursing homes are more at-risk for scabies.
Clean and sanitize your home. Keeping your home clean will help prevent the spread of scabies, especially if you or a family member have been previously infested. Wash all clothing, bedding, and towels used within the last 3 days on hot water, then dry it on the highest heat setting. If an item can’t be washed, place it in a closed plastic bag for at least 7 days to kill any mites or eggs. Scabies mites can only survive for 48 to 72 hours away from human skin, which is why keeping an item in a plastic bag will kill them. The day scabies treatment is started, vacuum all carpet and furniture in your home. Throw away the bag or empty and thoroughly wash the canister after you've finished vacuuming. If the canister is not removable, wipe it clean with a damp paper towel to remove any scabies mites. Don’t worry about treating your pets. The scabies mite cannot survive on other animals, and other animals cannot transmit scabies.



















Comments
0 comment