
views
- The habitat, water quality, and substrate you use depends on the specific species of crab, so don’t pour any old tap water into a rocky habitat.
- Crabs require specific temperatures (usually around 75–77 °F (24–25 °C)), so you may need a heat lamp or warming pad depending on where you’re keeping your crabs.
- Feed your crabs a diverse diet of frozen shrimp, seaweed, food flakes, or dry dog/cat food once a day.
- Crabs shed their exoskeletons every 8 weeks or so, but leave the exoskeleton in the tank so that the crabs can replenish their calcium levels.
Setting up the Crabitat
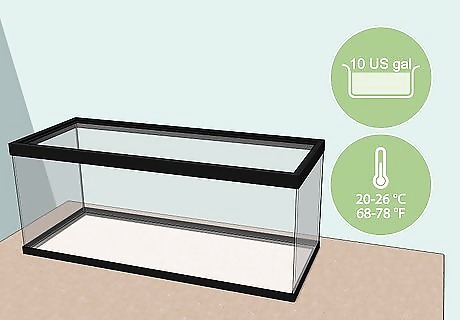
Place a 10 US gal (38 L) or larger tank in warm but not sunny spot. Plan to keep at least 2 crabs (since they’re social creatures) but never more than 1 male in the tank (to reduce the risk of fighting). If you want to keep more than 4 crabs, add 3 US gal (11 L) to the tank size per additional crab—for example, a 16 US gal (61 L) (or larger) tank for 6 crabs. If possible, choose a tank location that consistently stays between 68 and 78 °F (20 and 26 °C). Make sure the location is not exposed to direct sunlight, though, as it is harmful to crabs. These tank estimates are the same whether you plan to keep fiddler crabs (which are saltwater crabs) or land crabs (which are freshwater crabs). Halloween land crabs, rainbow land crabs, and fiddler crabs are the most common pet crab varieties.
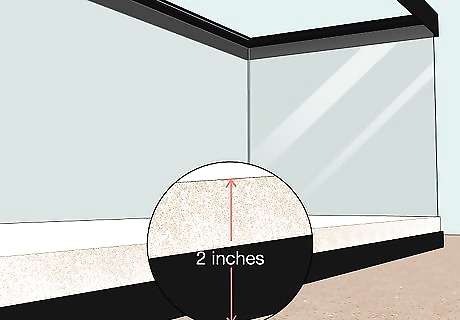
Add 2 in (5.1 cm) of aquarium sand as substrate. Pour an even layer over the entire bottom of the tank. Use sand that’s specifically designed for aquariums, which you can find at any pet supply retailer. Aquarium sand is screened, cleaned, and sanitized in ways that other types of sand may not be.
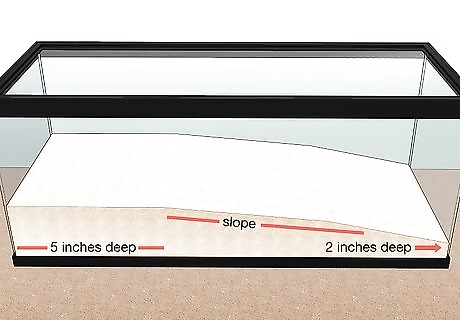
Add more sand to half of the tank to create a sloped shoreline. Pile up more sand in one-third of the tank bottom until it reaches 5 in (13 cm) in height. In the middle one-third of the tank bottom, create a sandy slope down to the 2 in (5.1 cm) substrate. In other words, if you’re looking at the tank from the side, the left (or right) one-third should have 2 in (5.1 cm) of sand in it, the right (or left) one-third should be filled with 5 in (13 cm) of sand, and the center one-third should slope between these sand heights. Tip: Keep in mind that the water in the tank should not be deeper than the smallest hermit crab, or about 1 in (2.5 cm), so adjust the level of the sand accordingly.
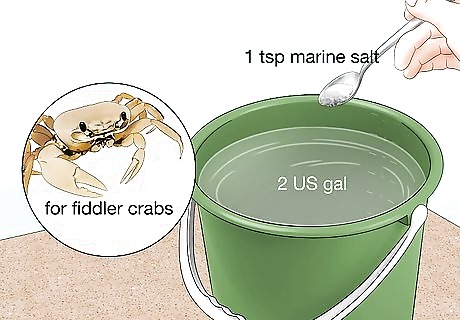
Make brackish water if you’re housing fiddler crabs. Add 2 US gal (7.6 L) of chlorine-free water to a clean bucket. Stir in 1 tsp (5 g) of marine salt, which is available at pet supply stores, until it dissolves. Use an aquarium hydrometer (also available at pet supply stores) to test the water. It should be at or very close to 25% salinity (or a specific gravity of about 1.02). Stir in more marine salt to raise the salinity, or add more water to reduce the salinity. You may need more or less water than this, depending on the size of the tank. Add the marine salt at the same ratio: 1 gram (0.035 oz) per 1.5 liters or 0.5 tsp per 1 gallon. Don’t use tap water without dechlorinating it first. Fiddler crabs are sometimes advertised as freshwater crabs by pet retailers, but they live much longer in brackish (low salt level) water.
Use dechlorinated freshwater if you’re keeping land crabs. Halloween land crabs and rainbow land crabs don’t require brackish water like fiddler crabs. But the water does need to be chlorine-free. Either buy jugs of chlorine-free water or use dechlorinating tablets (or other dechlorinating techniques) to remove chlorine from your tap water. The amount of water you’ll need depends on the size of the tank. A good starting estimate is 2 US gal (7.6 L).
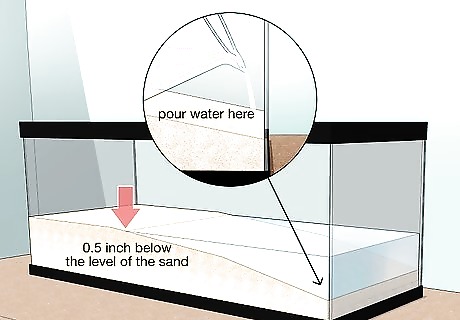
Add water to the tank until it’s nearly level with the sandy shore. Slowly pour or ladle the prepared water into the one-third of the tank bottom that only has 2 in (5.1 cm) of sand. Try not to disturb the sand more than is necessary. Keep adding water until it’s about 0.5 in (1.3 cm) below the level of the sand on the “shore” side—the side where the sand is about 5 in (13 cm) deep. A sandy shoreline is the natural habitat for fiddler crabs and land crabs. They should have access to both shallow water and sand that they can dig into.
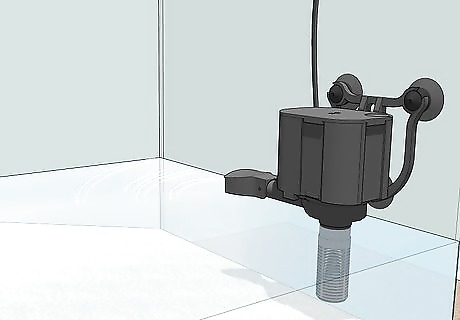
Set up an aquarium filter or an aeration pump in the water. Pet crabs require aerated water in order to thrive. A plug-in aquarium filter will both aerate the water and help keep it clean. The other option, a plug-in aeration pump, does not filter the water. Using an aeration pump requires you to change the tank water more frequently, but, if you do so, the crabs will be just as healthy and happy as if you use an aquarium filter. Aquarium filters and aeration pumps are available at pet supply retailers. Follow the specific setup instructions for your chosen model.
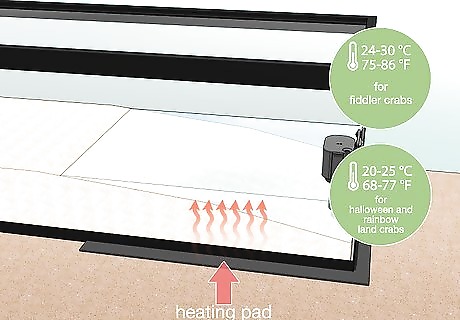
Use a heating element to maintain the right temperature for your crab species. Pet crabs are finicky about air temperature, so it’s best to install a heating element that ensures a consistent tank temperature. Use, for example, a temperature-controlled heat lamp or aquarium heating pad that goes on the side or bottom of the tank. Fiddler crabs require a temperature range of 75–86 °F (24–30 °C) Halloween and rainbow land crabs require a temperature range of 68–77 °F (20–25 °C)
Feeding and Entertaining the Crabs

Feed the crabs a wide-ranging diet once per day. Crabs are true omnivores that will eat practically anything. Scatter the food over the dry sand once per day. If all the food is gone in less than an hour, start providing more; if the food is still there after 2-3 hours, start providing less. Try offering crab claw-sized bits of foods like the following: Frozen shrimp and plankton from the pet supply store. Dry or fresh seaweed. Lettuce, zucchini, apples, and potatoes. Raw fish. Hermit crab food pellets. Fish food flakes. Dry dog or cat food.
Let the crabs nibble on molted shells or cuttlefish bones for calcium. Crabs shed their exoskeletons (shells) about every 8 weeks and grow a replacement—this process is called molting. The molted exoskeleton is a great source of calcium, so leave it in the tank for 1-2 weeks and let the crabs nibble on it if they want. During times when there are no molted exoskeletons in the tank, add some cuttlefish bones, which are available at pet supply stores.
Add plastic plants, toys, and objects to the tank to entertain the crabs. While live plants may look nice in the “crabitat,” crabs are omnivores and tend to kill off live plants fairly quickly. Instead, use aquarium-safe artificial plants and other objects of interest to decorate the tank. Crabs don’t need hiding spaces, since they dig into the sand to conceal themselves. They also don’t need specific toys to occupy them. Just try different items and see which seem to appeal to the crabs.Warning: Don’t try to get the crabs out to play with them. Entertain yourself simply by watching them!
Maintaining the Crabitat
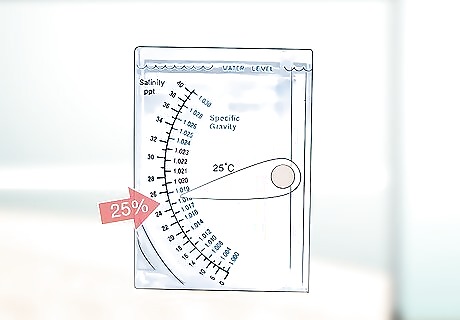
Test the water salinity (if applicable) and pH at least once per week. Use your hydrometer to confirm that the water is still at roughly 25% salinity (or 1.02 specific gravity). Use a pH testing kit (either digital or chemical, both available at pet supply stores) to check the acidity of the water. For saltwater crabs, the pH should be between 8.0 and 8.3; for freshwater crabs, it should be between 6.5 and 7.5. Add a bit more water or marine salt to adjust the salinity, if needed. Add about 0.25 tsp (1.25 g) of baking soda per 1 US gal (3.8 L) of water to increase the pH, if necessary.
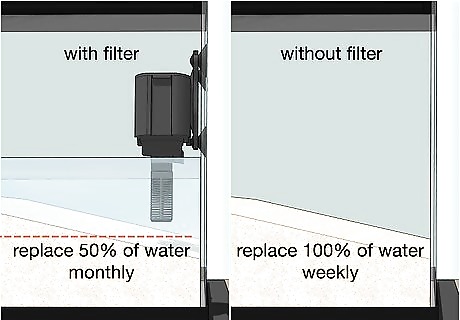
Replace half the water monthly (with filter) or all of it weekly (no filter). If your tank has a filter, remove 50% of the water once per month or 25% of it twice per month. Do this by using a ladle or large syringe to remove the water, then add water that is at the tank’s temperature and that has been prepared (for salinity, pH, etc.) according to the needs of the crabs in the tank. Tip: If your tank does not have a filter, remove as much of the water as you can with a ladle and large syringe, then replace it with properly prepared water. Do this once per week.
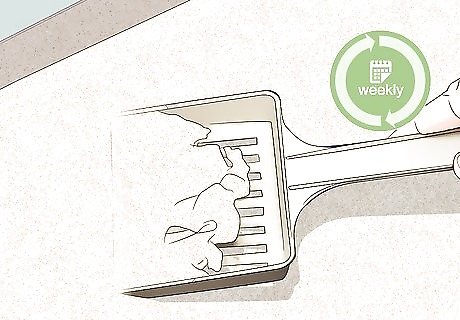
Clean the substrate surface with a kitty litter scoop every week. Skim the sandy surface with the scoop so that you pick up the very top layer of sand and any feces or food waste present. Shake the scoop lightly so that the sand falls through the slits or holes, then discard the waste. Clean the sand more frequently if the tank tends to develop an unpleasant odor during the week.
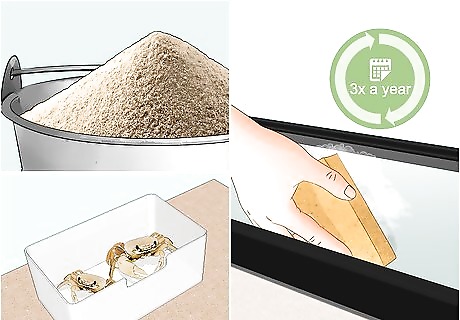
Empty, clean, and refill the tank completely 3 times per year. Move the crabs to individual containers that they can’t escape from, like high-sided plastic storage containers without lids. Return them to the tank as soon as you complete all of the following cleaning measures: Remove all plastic plants, toys, etc., wipe them down with a rag soaked in a 3% bleach solution (available at pet supply stores), rinse them with clean water, and dry them with a clean towel. Remove and discard all the water and sand in the tank. Clean all the interior surfaces of the tank with the 3% bleach solution, rinse them thoroughly with clean water, and dry them completely with clean towels. Prepare the tank as you did for the original setup, using new sand and properly-prepared water. Make sure the water and the tank interior are within the appropriate temperature range.

















Comments
0 comment