views
X
Trustworthy Source
Mayo Clinic
Educational website from one of the world's leading hospitals
Go to source
Many countries have reported Zika outbreaks, but by protecting yourself from mosquito bites and reducing your environmental risks, you may be able to prevent Zika.
Protecting Yourself from Mosquito Bites
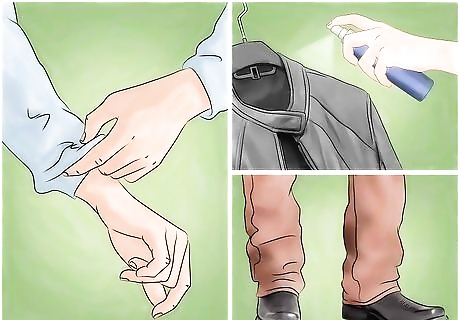
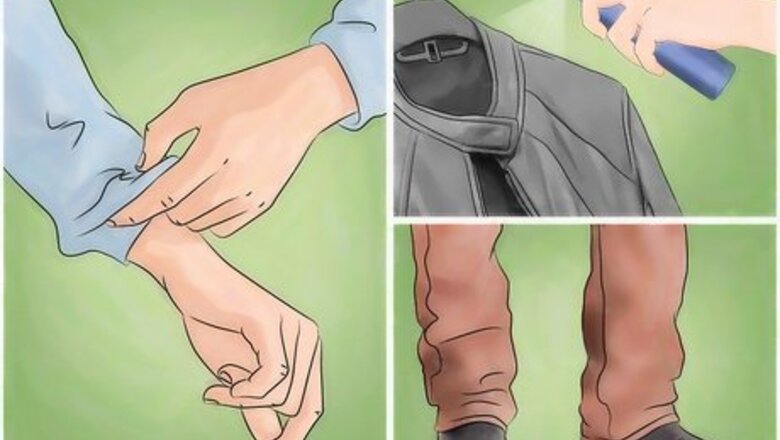
Cover as much of your skin as possible. Since mosquito bites are the main source of infection, you will need to cover as much of your exposed skin as possible. Wear long sleeves, long pants, socks, and closed-toe shoes when you are in mosquito-infested areas. You may even want to consider wearing a mosquito net hat when you are out. You can also treat your clothing with permethrin or purchase permethrin-treated clothing to add an extra layer of protection.
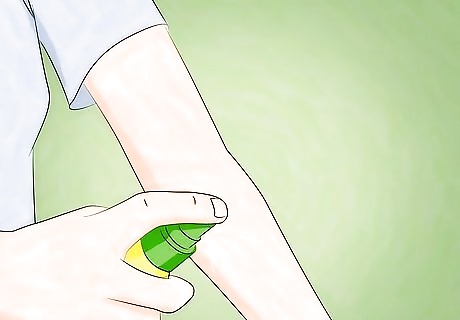
Apply an EPA-registered insect repellent. Applying insect repellent to your body is another effective measure. Make sure that the insect repellant that you choose is Environmental Protection Agency or EPA-registered. You can find this information on the label. Always read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for use. Reapply the insect repellant as often as the package suggests. Apply sunscreen before you apply insect repellent. Apply insect repellent over your clothes, not under them.
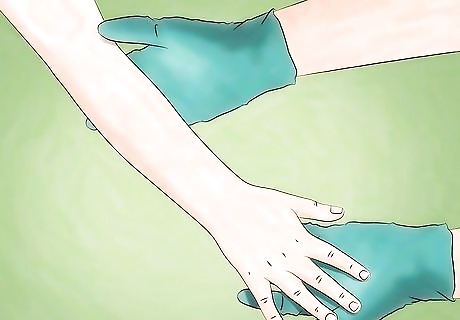
Wear gloves if you need to clean up bodily fluids. If you are caring for someone who has Zika, then make sure that you wear gloves and wash your hands well if you need to clean up the infected person’s blood or bodily fluids. A person may have the Zika virus in their blood for about one week.
Use protection when you have sex. Zika can be transmitted through bodily fluids, such as semen and blood, so it is important to use protection. Make sure that you protect yourself by wearing a condom every time you have sex. Use a condom even if your partner seems healthy. Remember that in most cases, Zika has no symptoms.

Take extra precautions if you are pregnant. Pregnant people may pass the virus onto an unborn child, but it is rare. There have also been some reports of birth defects in babies born to those who contracted the Zika virus while pregnant. For these reasons, pregnant people should be even more cautious and do everything possible to prevent mosquito bites. Keep in mind that the link between Zika virus and the birth defect microcephaly is not fully understood. This condition results in an abnormally small head circumference as well as some developmental delays. In some cases, microcephaly can even be fatal.
Reducing Environmental Risks

Stay in places with air-conditioning or window screens. Even if you are inside, it is possible to be bitten by a mosquito that has entered your home. Try to prevent mosquitoes from getting into your home by using air-conditioning or window screens instead of just opening windows. If you are travelling to a high-risk area, then try to stay in hotels that have air conditioning and/or screens on all of the windows. If possible, run an air-conditioner when the weather is warm instead of opening windows and running fans. If you do not have an air-conditioner, then put up window screens on all of the windows in your home. Make sure that there are no holes or tears in the screens through which mosquitoes may enter.
Sleep with a mosquito net. Mosquito nets can protect you from bites while you sleep. Inspect your mosquito net to make sure that it is free from holes or tears. Also, make sure that it touches the ground and goes all the way around your bed. Some mosquito nets are even treated with permethrin, which offers even more protection from mosquitoes during the night.

Remove standing water. Mosquitoes breed and lay eggs in standing water, which can increase the mosquito population in your area and increase your chance of contracting Zika. Make sure that you remove any items that might collect water, such as buckets, old tires, or flower pots. Fill in small puddles with sand or dirt to eliminate this potential breeding ground as well.
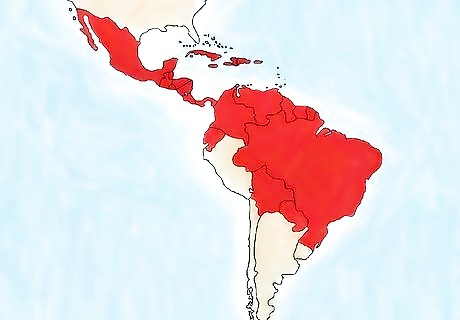
Steer clear of high-risk areas if possible. To prevent the Zika virus, you may want to consider postponing travel to areas where there are outbreaks. Pregnant people are strongly encouraged to avoid high-risk areas due to the risks that the virus poses to unborn babies. Places with recent outbreaks of Zika virus include: Bolivia, Ecuador, Guyana, Brazil, Colombia, El Salvador, French Guiana, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Panama, Paraguay, Suriname, Venezuela, Barbados, Saint Martin, Haiti, Martinique, Puerto Rico, Guadeloupe, Samoa, and Cabo Verde.


















Comments
0 comment