
238
views
views
The "su" command, which stands for "switch user" or "substitute user," makes it easy to change to another user in Linux. Or, if you just want to execute a command as another user without logging in as them, you can use "sudo," or "superuser do." Read on to learn how.
- To become another user in Linux, use su - <username>.
- To run commands as a different user, use sudo -u <username> <command>.
- In the GNOME desktop environment, you can change users in the System menu > Power Off / Log Out > Switch User.

Click the system menu. It's at the top-right corner of your desktop—where you'll see the network icon, volume, and battery.

Click Power Off / Log Out. This expands more options.
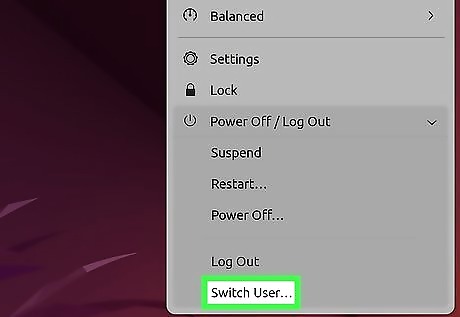
Click Switch User and enter that user's login information. As long as you have at least one more user added to your Linux system, you'll see the Switch User option. When you switch users, the applications you were running will continue to run in the background. You can easily switch back and forth between users as needed.

















Comments
0 comment