
views
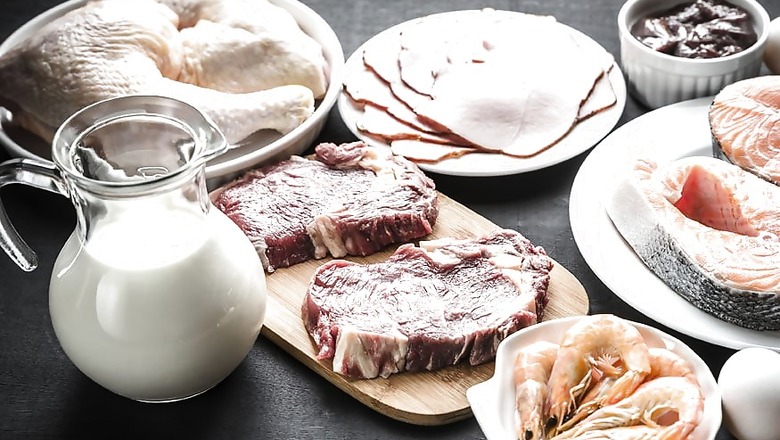
Popular with athletes and models, the ketogenic diet is high in fat and very low in carbohydrates. Carol Johnston, a director of the School of Nutrition and Health Promotion at Arizona State University, explains why it is so successful when it comes to weight loss.
On the ketogenic diet, 75 percent of your calories come from lipids. Dieters eat meats, poultry, fish, shellfish, eggs, butter, oils, oleaginous fruits, avocado, low-carbohydrate like green leafy vegetables (spinach, kale and lettuce) -- and hard cheeses. Other dairy products, milk and full-fat yoghurts can be consumed in moderation.
How does the body respond to a lack of carbohydrates?
Cells which no longer have an available source of carbohydrates have to find a new source of energy. The body initiates a process that is the same as that triggered by fasting: it calls on "ketone bodies", three types of compounds that result from the conversion of fatty acids in the absence of glucose. Two of these ketone bodies are used as an energy source by the heart and the brain, the third is eliminated.
How does the ketogenic diet cause weight loss?
The low-carb diet is very high in fat, which helps people feel full, and thus eat less. Weight loss occurs more rapidly than with a sudden reduction in calories. As a result, people go the distance without too much effort, and are more likely to stick to the diet.
"In the first few days, a person can experience a significant loss of water weight, because when carb intake is restricted for a few days, glycogen stores in the muscle are reduced," explains Carol Johnston, director of the School of Nutrition and Health Promotion at Arizona State University in the United States.
Risks that should not be ignored
The risks associated with a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet are significant. According to Johnston, it can result in increased blood levels of triglycerides (a marker of elevated cardiovascular risk), increased urinary uric acid (which may lead to the formation of kidney stones), and lethargy. There is also an increased risk of negative impact on bone health.
Are carbs really bad for health?
"Carbs are important for our brain and muscle health,” points out Johnston. "Our brains rely entirely on glucose for energy production -- they can't get it from fat -- making the consumption of some carbs necessary. Our muscles can use either glucose or fat for energy, but during high-intensity exercise, they prefer glucose."
The problem with carbs is the excessive consumption of sugar, which is converted into fat and causes weight gain.
"Long-term lifestyle changes" are the best recipe for sustainable weight loss, said Johnston. "For weight loss, the most important thing is to stick to the diet you have chosen."













Comments
0 comment